Fig. 1.
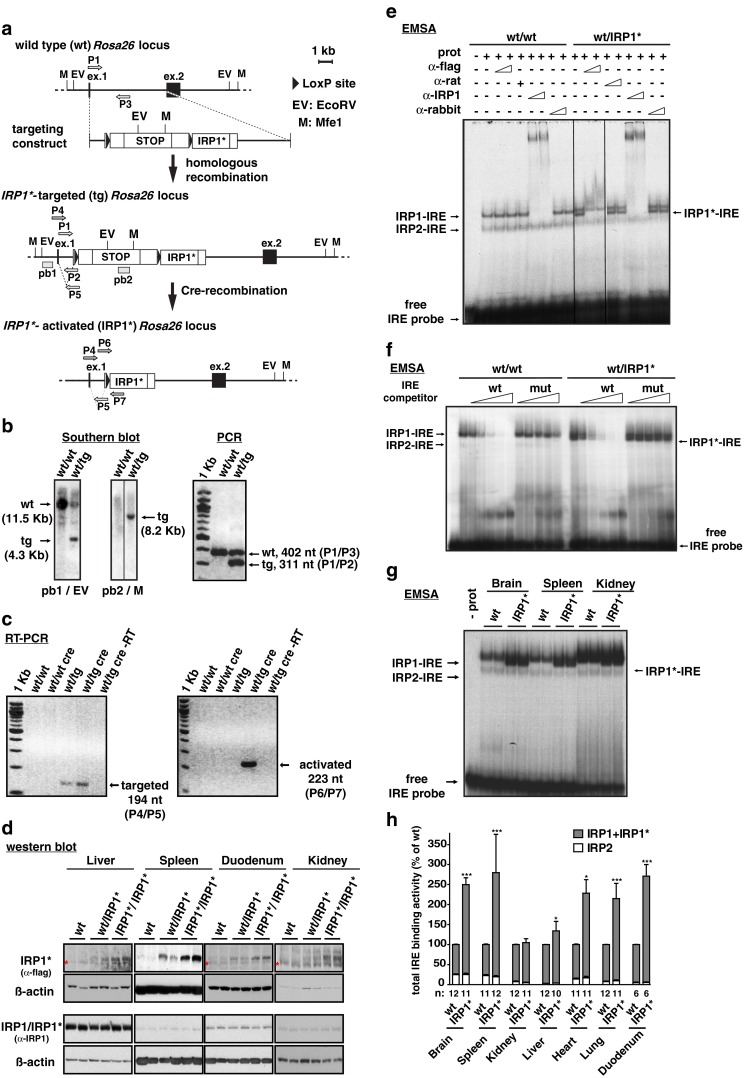
Targeting of the Rosa26 locus with a Cre/Lox inducible IRP1* expression construct and ensuing gain of IRP1 activity in mouse tissues. a Schematic representation of the wild type, IRP1*-targeted and IRP1*-activated Rosa26 locus and of the targeting construct. Restriction sites for EcoRV (EV) and Mfe1 (M) are indicated. The external probe, pb1 (recognizing the first exon of the Rosa26 locus) and the internal one, pb2 (recognizing the stop cassette) are shown. Primers used to assess Cre-mediated recombination of the targeted allele and for routine genotyping are indicated. b Southern blot to verify bona fide targeting of the Rosa26 locus (left panel). Restriction enzymes and probes used are specified below the panels; genotypes are indicated above each lane. Multiplex-PCR for routine detection of the targeted Rosa26 locus (right panel); primer pairs used are indicated on the right. c RT-PCR to confirm Cre-mediated recombination of the Rosa26 locus using cDNA from duodenum. Primer pair P4/P5 is specific for the targeted locus (left panel), but does not discriminate the recombination event. P6/P7 is specifically designed to detect the activated allele (right panel). d Representative western blot showing IRP1* or IRP1 + IRP1* (IRP1/IRP1*) expression in spleen, duodenum, kidney, and liver extracts. An anti-FLAG-tag antibody was used to detect IRP1*, one raised against IRP1 recognizes both IRP1 and IRP1*. In liver, duodenum, and kidney samples, a cross-reacting band is marked with an asterisk. β-actin was used as a standard. e EMSA analysis to assess the IRE-binding activity of IRP1*. Cytoplasmic extracts from ileum were used. An anti-FLAG antibody was used to identify the IRP1*-IRE complex by supershift. An antibody recognizing both IRP1 and IRP1* was used to supershift both IRP1- and IRP1*-IRE complexes. Normal rat and rabbit IgGs, respectively, were used as a negative control. f Competitive EMSA using cytoplasmic extracts from ileum. Molar excess of an unlabeled wild type or mutant FTH1 IRE competitor RNAs over the radiolabeled FTH1 IRE probe was used. g Representative EMSA showing the degree of gain of IRP1 activity in cytoplasmic extracts from the brain, spleen, and kidney. Wild type and IRP1* homozygous animals were analyzed; genotypes are indicated above each lane. h The histogram represents the relative quantification of a series of EMSAs performed on a larger number of animals using cytoplasmic extracts from the brain, spleen, kidney, liver, heart, lung, and duodenum. Sample size is indicated (n). *p<0.05; ***p<0.001
