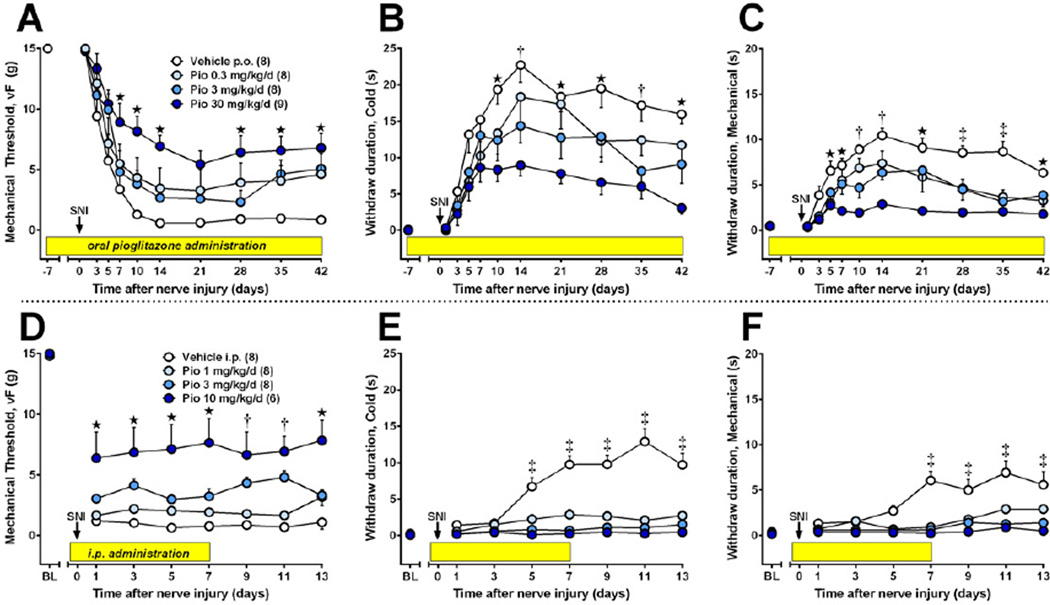
Figure 1. The development of nerve injury-induced hypersensitivity is reduced by pioglitazone.
Pain-related responses to plantar application of von Frey hairs (A), acetone (B), or pin prick (C) were monitored from 7 d prior to 6 wk after spared nerve injury (SNI, t = 0 d, arrow). After baseline measurements, pioglitazone (mixed with rat chow in concentrations yielding daily doses of 0 to 30 mg/kg/day) was administered throughout the rest of the study (yellow bars). Oral pioglitazone dose-dependently reduced the development of hypersensitivity (n = 8–9). (D–F) Intraperitoneal injections began 15 min prior to SNI (arrow) and continued twice daily for 7 days (yellow bars). Pioglitazone reduced the development of hypersensitivity to vF, and prevented the development of hypersensitivity to cold and prick (n = 6–8). Values represent mean ± SEM. Statistical significance (p<0.05 by Bonferroni post-tests after repeated measures 2-way ANOVA) between vehicle and high (★), high + medium (†), or high + medium + low (‡) doses of pioglitazone.