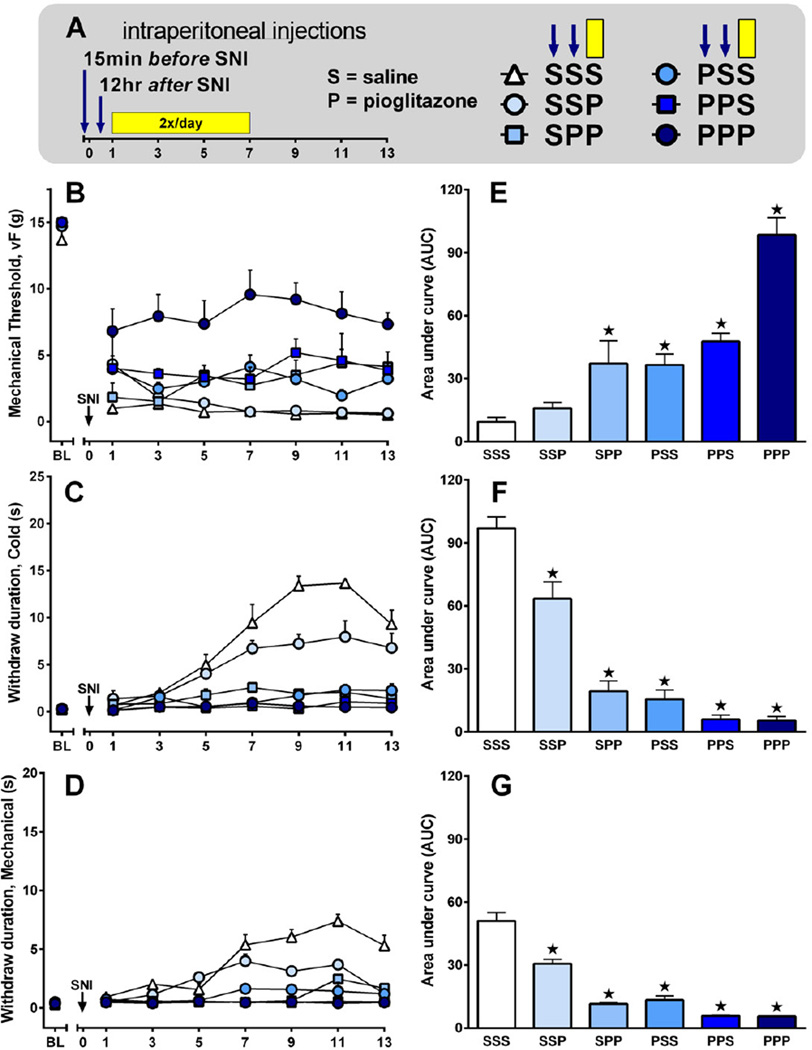
Figure 5. Preemptive and post-surgery treatment with pioglitazone reduces neuropathic pain.
(A) Saline (S) or 10 mg/kg/day pioglitazone (P) was administered at one or more of the following times relative to SNI surgery in varying combinations: a single injection 15 min before SNI (first arrow: S or P); a single injection 12 hr after SNI (second arrow: S or P); or twice-daily injection begun 24 hr after SNI and lasting through day 7 (yellow bar: third S or P). For example, the first P in PPP reflects injection 1 (15 min prior to SNI), the second P in PPP represents injection 2 (12 hr after SNI), and the third P in PPP represents twice-daily injections (24 hr to 7 d after SNI) (n = 6 per group). (B–D) Line graphs illustrating behavioral responses to von Frey (B), acetone (C), or pin prick (D) stimuli applied to the ipsilateral plantar hindpaw. (E–G) AUC bar graphs summarizing the effect of pioglitazone (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett test versus SSS) on mechanical threshold [F(5, 35)=23, p<0.0001], cold withdraw duration [F(5, 35)=56, p<0.0001], and pin prick withdraw duration [F(5, 35)=67, p<0.001]. Values represent mean ± SEM. (★) denotes significant difference (p<0.05 vs. vehicle by Bonferroni post-tests following repeated measures 2-way ANOVA).