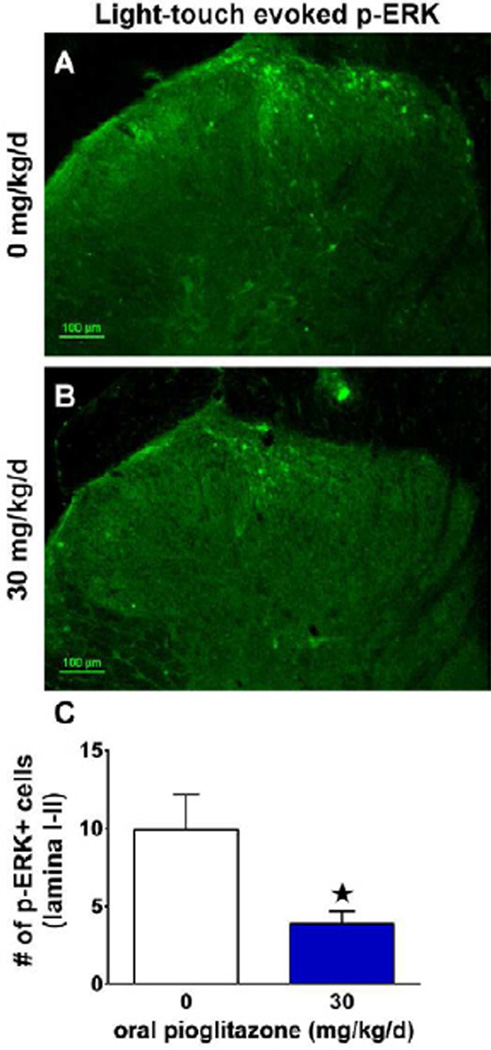
Figure 7. Pioglitazone reduced light touch-evoked spinal ERK activation after SNI.
(A) Representative image 42 d after spared nerve injury showing that mechanical stimulation of the sural receptive field ipsilateral to injury (every 5 seconds for 5 minutes) resulted in a greater number of p-ERK positive profiles than the unstimulated contralateral dorsal horn (p<0.01; data not shown) in rats consuming standard rat chow (0 mg/kg/d pioglitazone). (B) Representative image showing a reduced number of p-ERK+ profiles in rats that were provided with 30 mg/kg/d pioglitazone in the rat chow. (C) Quantification of the number of p-ERK+ profiles in rats fed standard chow versus pioglitazone chow revealed a significant reduction in light touch-evoked spinal ERK activation (n = 6 per group). (★) denotes significant difference (p<0.05 via post-hoc t-tests). Scale bar = 100µm.