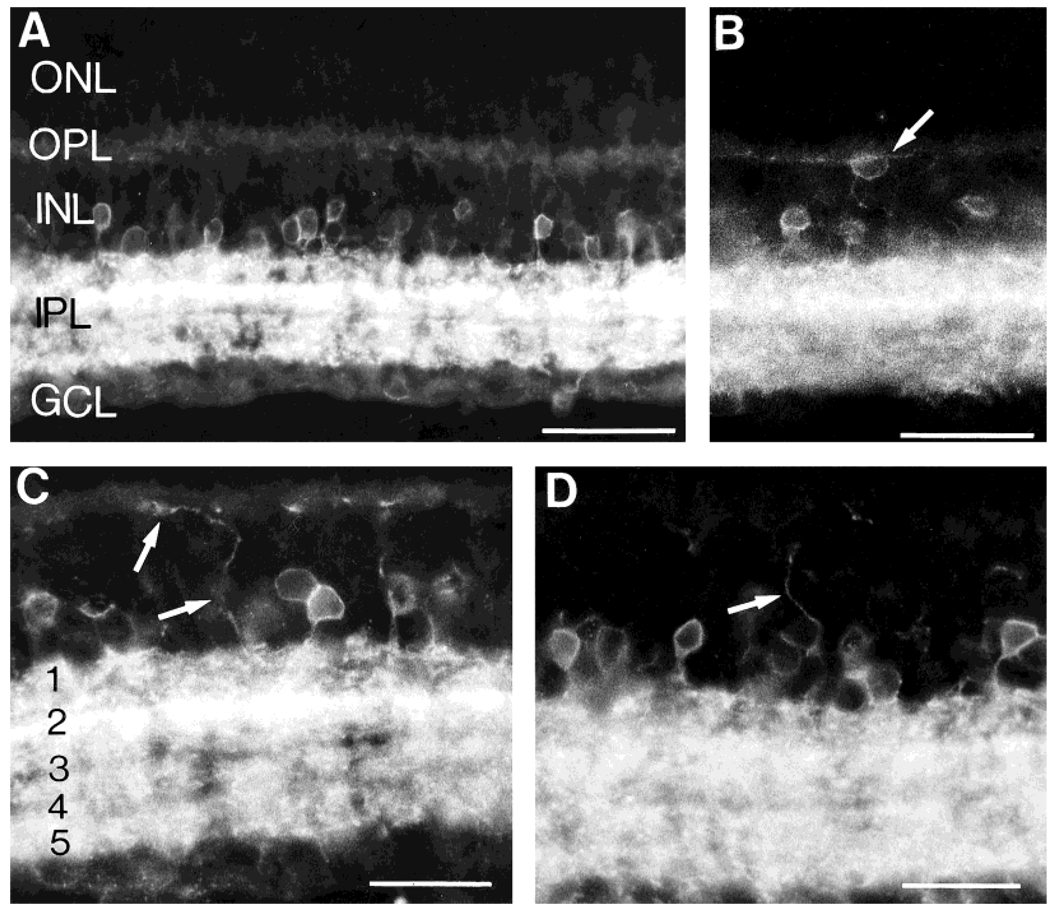
Fig. 1.
Neurokinin 1 (NK1) immunofluorescence in retinal sections cut perpendicular to the vitreal surface. A: NK1-immunoreactive (IR) cells are mainly located in the proximal inner nuclear layer (INL), whereas their processes are densely distributed to all laminae of the inner plexiform layer (IPL). B: Rare NK1-IR cells (arrow) are observed in the outer INL. C,D: NK1-IR processes (arrows) running in the distal INL and arborizing in the outer plexiform layer (OPL). In C, the IPL laminae are numbered (1–5): the highest density of NK1-IR processes is in lamina 2. GCL, ganglion cell layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. Scale bars = 50 µm in A and B, 30 µm in C and D.