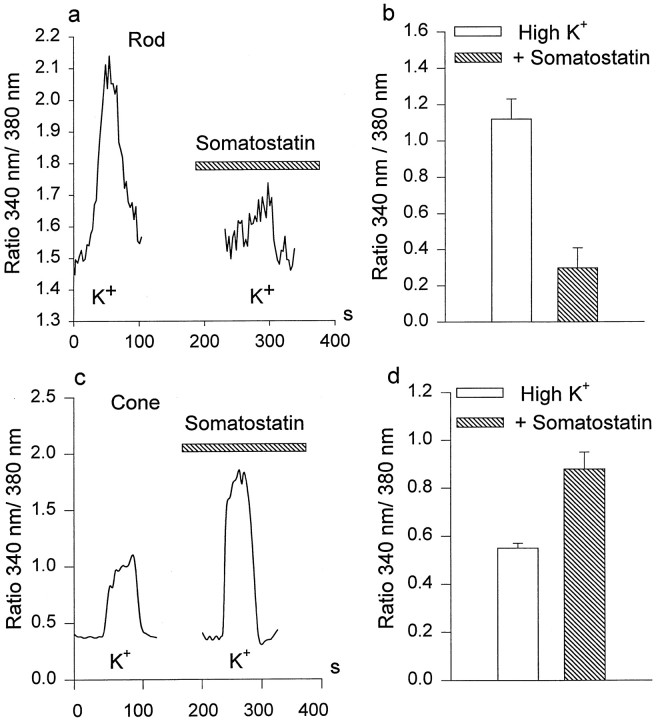
Fig. 7.
Effects of somatostatin on K+-induced Ca2+ accumulation in rods and cones. a, c, KCl (100 mm) was used to stimulate Ca2+ entry in the absence and the presence (hatchedhorizontalbar) of 0.5 μm somatostatin in rods (a) and cones (c). Somatostatin reduced Ca2+ accumulation in rods but increased it in cones. b, d, Histograms summarize the somatostatin-induced inhibition of Ca2+ accumulation in rods (b; n = 5) and its enhancement in cones (d; n = 5).Verticalbars show the mean values ± 1 SE.