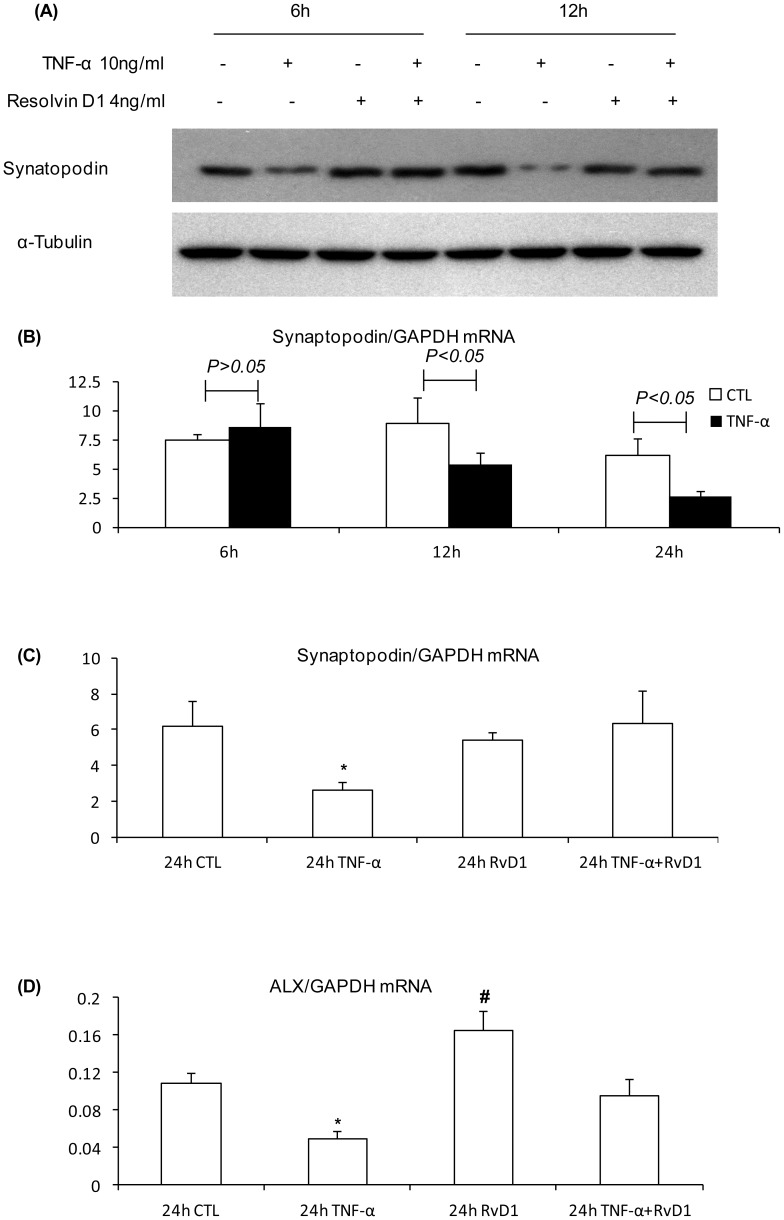
Figure 9. RvD1 protected TNF-α-induced loss of synaptopodin in mouse podocytes.
(A) Podocytes were cultured for 6 or 12 hr with TNF-α, RvD1 or both together. The Western blot shows protein levels for synaptopodin and the α-tubulin control. (B) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of synaptopodin mRNA levels shows no change in mRNA levels 6 hr after TNF-α treatment, and a reduction in mRNA levels after 12 and 24 hr. (C) Real-time RT-PCR analysis shows RvD1 (4 ng/ml) can prevent the down-regulation of synaptopodin mRNA seen with 24 hr treatment with TNF-α (10 ng/ml). (D) Real-time RT-PCR analysis shows podocytes express ALX mRNA. This is down-regulated 24 hr after TNF-α treatment, which is prevented by RvD1, and RvD1 by itself up-regulates RLX mRNA levels. *P<0.05 vs 24 h control (CTL), or 24 h RvD1, or 24 hTNF-α+RvD1; # P<0.05 vs 24 h CTL and vs 24 h TNF-α+RvD1.