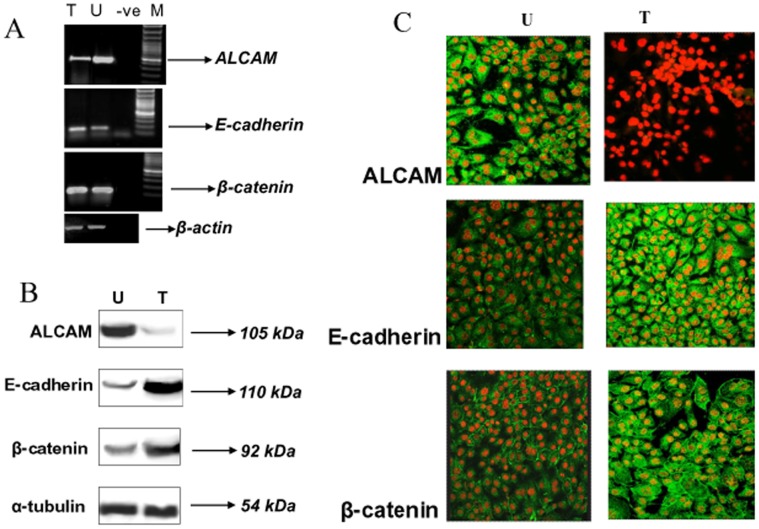
Figure 4. siRNA knockdown of ALCAM and its effect on E-cadherin and β-catenin.
A: RT-PCR analysis of ALCAM (490bp), E-cadherin (160bp) and β-catenin (167bp) amplicons in siRNA transfected (15 nM, lane T) and control (lane U) SCC-4 cells at 48 h post transfection. β-actin (421bp) transcript was used as control for normalization. B: Immunoblot analysis of ALCAM, E-cadherin and β-catenin proteins in SCC-4 cells silenced for ALCAM. SCC-4 cells treated with ALCAM siRNA (15 nM) for 48 h and untreated cells were immunolabelled with respective antibodies and developed using ECL. 7-folds decreased levels of ALCAM (105 kDa) were observed in ALCAM-depleted transfectants (lane T) as compared to untreated SCC-4 cells (lane U); 3-folds increased levels of 110kDa E-cadherin protein (lane T) were observed in ALCAM-depleted transfectants as compared to the untreated SCC-4 cells (lane U); 2-folds increased levels of 92kDa β-catenin protein (lane T) were observed in ALCAM-depleted transfectants as compared to the untreated SCC-4 cells (lane U); α-tubulin (54 kDa) was used as control protein for quantitation. C: Expression of ALCAM, E-cadherin, and β-catenin proteins in ALCAM silenced SCC-4 cells. Cells grown on coverslips were treated with ALCAM siRNA, processed for confocal microscopy, immunolabelled with respective antibodies to ALCAM, E-cadherin and β-catenin proteins followed by FITC conjugated secondary antibody (Green fluorescence), nuclei were counterstained with PI (red fluorescence) (Original Magnification X 400).