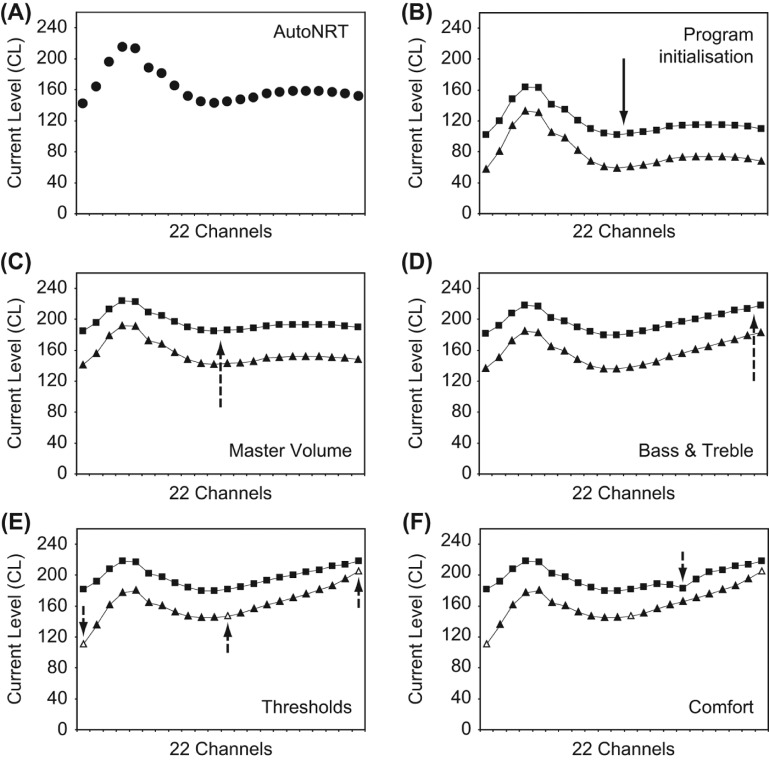
Figure 1.
The fitting methodology and its control on program T- and C-levels (triangle and square markers, respectively). A. AutoNRT ECAP thresholds (circle markers) are measured (here at 22 electrodes intraoperatively). B. A program is instantly initialized, with an average dynamic range of 40CL, Master Volume set to 120 (inaudible or very soft), and Bass & Treble set to 0. C. Master Volume is gradually raised in the presence of live audio until comfortable. D. Bass & Treble are adjusted if desired. E. Three thresholds are measured if desired, bending the T-level profile. F. A Comfort check is performed if desired, adjusting selected bands of levels. Blocks A–D comprise the Remote Assistant Fitting methodology, and blocks A–F the Nucleus Fitting Software methodology. The deviation in levels at low frequencies is atypically large, chosen here to demonstrate the effect of profile scaling: the C-level profile is flatter than the T-level profile, and both profiles flatten when Master Volume is raised.