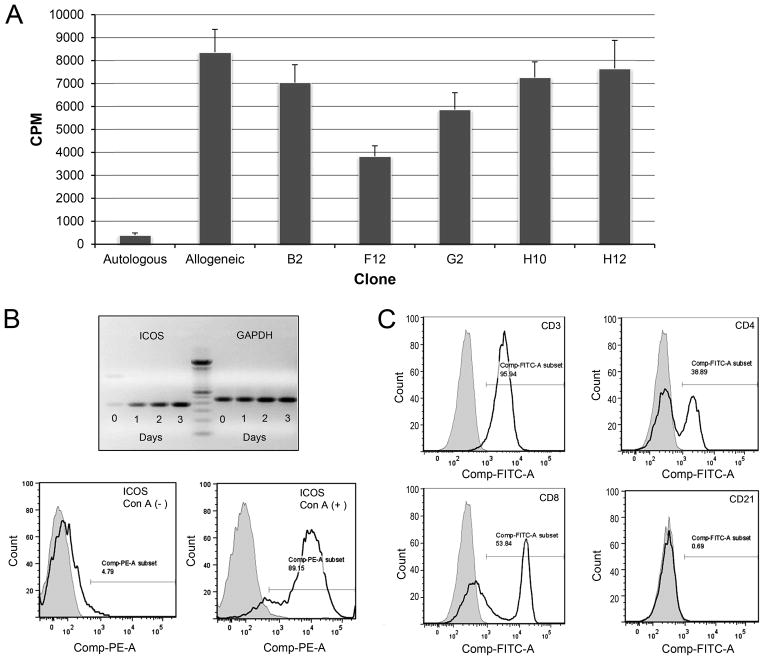
FIGURE 1. Anti-caICOS clone selection and ICOS expression on canine lymphocytes.
A) Five anti-caICOS mAbs were purified from hybridoma supernatants and added at 10 μg/ml to 7-day MLR comprised of PBMC from DLA-nonidentical dogs. Results are representative of two experiments and presented as counts per minute (CPM) of 3H-thymidine. B (upper) Real time PCR showing ICOS and GAPDH (control) mRNA expression in Con A activated PBMC over a three-day period. A 100 bp ladder (center) marks the expected size of the extracellular domain of canine ICOS at 363 bp. B (lower) Histogram showing ICOS-PE expression on naive and 3–day Con A activated canine CD3+ lymphocytes. (A and B representative of 4 dogs in 4 experiments) C) ICOS expression on PBMC from normal dogs cultured with Con A for 3 days. The histograms show ICOS+ on CD3+ gated cells (upper left panel); with this population stained with CD4-FITC and CD8-FITC antibodies (panels upper right and lower left respectively) or the B-cell marker, CD21-PE (lower right). Shaded regions represent isotype control fluorescence intensity. (Figure representative of 3 experiments using 3 different dogs).