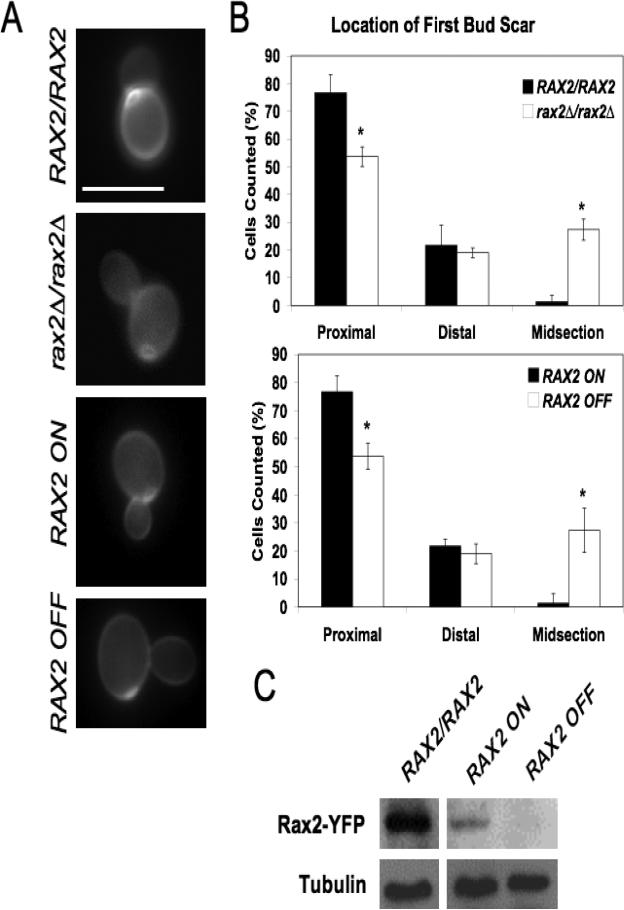
Fig. 1. Rax2 is important for bud-site selection during C. albicans yeast-form growth.
(A) Representative fluorescence images of site of first budding event in wild-type (WT; BWP17), rax2Δ/rax2Δ (CA10500), and control strains allowing regulatable expression of RAX2 from the MET3 promoter (CA12041) stained with calcofluor white. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of position of first bud scars positions (after 2h of growth at 28°C in SDC) in the strains depicted in part (A). Data are presented as percentages of total cells counted ± SEM. (C) Western blot of whole protein lysates, reacted with anti-GFP antibody, from a WT strain expressing Rax2-YFP (CA10031) and a control strain allowing regulatable expression of Rax2-YFP from the MET3 promoter (CA11891). Tubulin levels for each condition are included as an indication of total protein load.