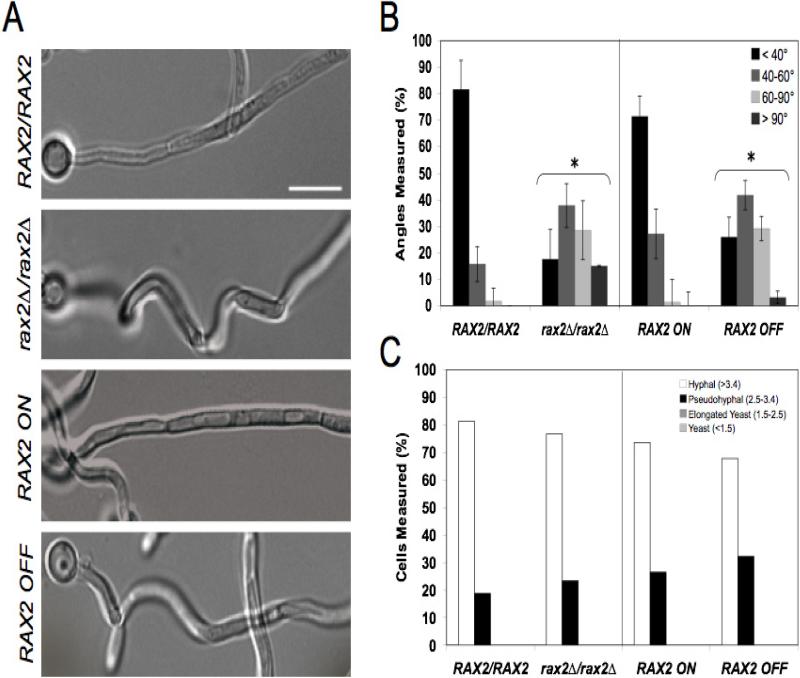
Fig. 3. RAX2 is important for maintaining linear hyphal growth, but not for overall hyphal morphology.
(A) Representative DIC microscopy images of cell growth trajectories in strains listed and grown as described in Fig. 2A. In the absence of RAX2 hyphae are visibly curvier. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Quantification of hyphal angles. The first angle of each hypha was measured using the MetaMorph® Angle Measurements tool and the mean angle ± SEM for each strain/condition is shown. n~30 hyphae for each strain and each assay was performed in triplicate. *, comparisons between strains lacking Rax2 and their isogenic Rax2-expressing parent strains were statistically different at the p<0.001 level. (C) Morphology Index (MI) values of WT the strains depicted in A. The classic morphology definitions with respect to morphology index (Merson-Davies and Odds, 1989) are indicated on the graph. n~30 hyphae for each strain.