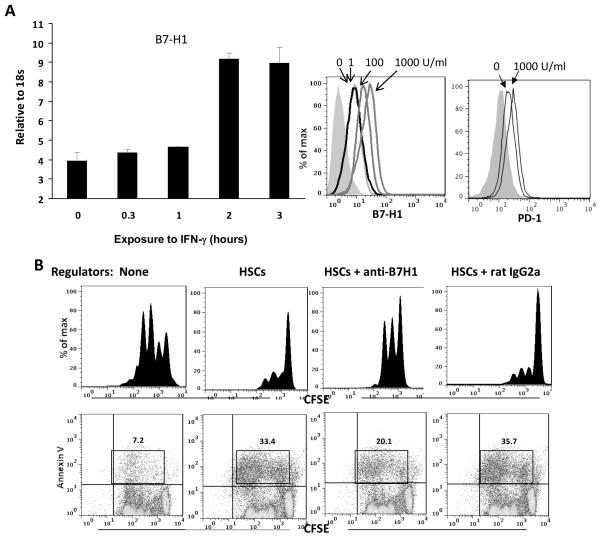
Figure 4. Regulation of B7-H1 expression on HSCs and its role in induction of T cell apoptosis.
(A) Expression of B7-H1 on HSCs is enhanced by IFN-γ stimulation. HSCs were incubated with IFN-γ (100 U/ml) for various (indicated) durations. B7-H1 expression was analyzed by q-PCR (left panel). HSCs were exposed to graded concentrations of IFN-γ for 18 hours and stained with anti–B7-H1 or anti-PD-1 mAb for flow analysis, and demonstrated as histograms. The filled area represents isotype control (right panel). (B) HSCs-induced T cell inhibition is mediated by B7-H1 ligation. Inhibition of (1×105) were added to HSCs (1×104) and cultured for 3 days. Irradiated HSCs were added at the beginning of a CFSE labeled PBMC-derived T cell culture (at a ratio of 1:10), the proliferation of which was elicited by anti-CD3/CD28 beads. T cell proliferative response was determined by CFSE dilution assay gated in CD3+ cells. Apoptotic activity was analyzed by staining for annexin V expression. The number is percentage of annexin V+ dividing cells. Data are representative of three separated experiments.