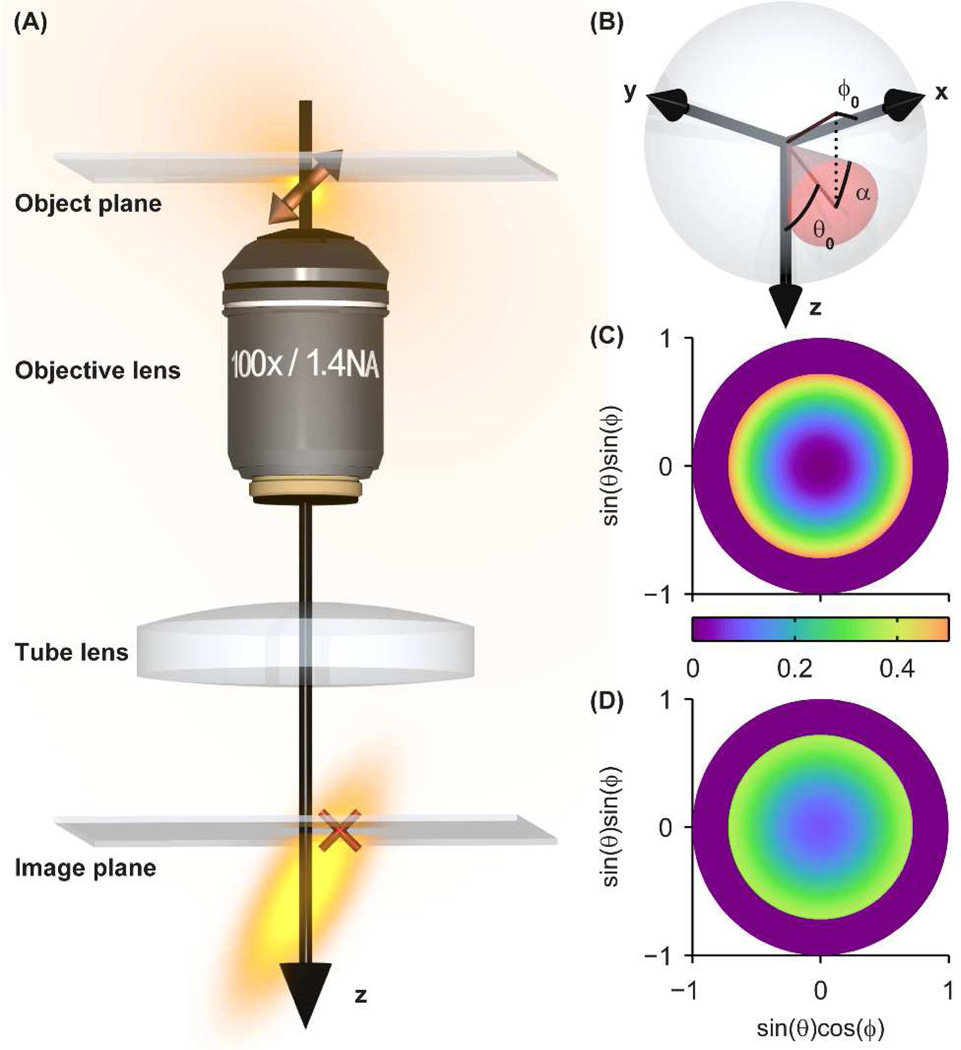
Figure 1.
Overview of SM dipole emission and rotational diffusion. (A) The emission pattern of a fixed SM in the object space of a microscope, consisting of an objective lens and tube lens, creates an asymmetric elongated 3D PSF in the image space. Slight defocus (here illustrated with the emitter below the focal plane) causes the lateral (x,y) photon distribution in the image plane to be shifted (red cross) relative to the true molecular position in the object plane. (B) Our model of rotationally diffusing SMs involves confinement to a hard-edged cone of orientation (θ0, ϕ0) and half angle α in spherical orientation space. The (C) photon absorption probability density and (D) image weighting factor η(θ, ϕ) for a cone of orientation (θ0, ϕ0) = (0°,0°) pointing toward the viewer and half angle α = 45° are plotted in two-dimensional orientation space with definitions given by the axis labels.