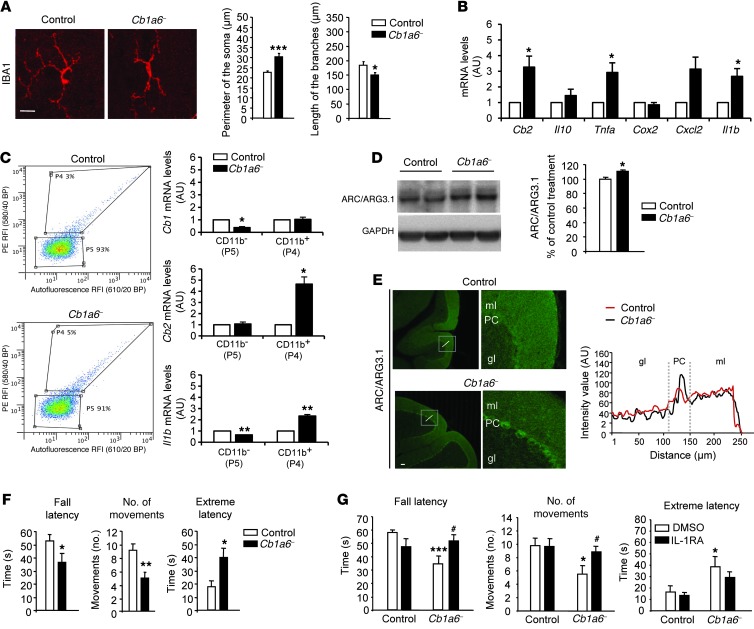
Figure 8. CB1R downregulation in the parallel fibers is sufficient to trigger cerebellar neuroinflammation and IL1-RA–sensitive motor coordination impairment.
(A) Morphological analysis of IBA1+ cells in the cerebellar cortex of Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 4–5 per group, 6 cells per mouse). Scale bar: 25 μm. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 versus control. (B) Analysis of Cb2r mRNA expression by qRT-PCR and inflammation-related genes in the cerebellum of Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 5 per group). *P < 0.05 versus control. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of CD11b expression and qRT-PCR analysis of Cb1r, Cb2r, and Il1b of acutely dissociated cerebellar cells from Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 3–4 per group). *P < 0.05 versus control. (D) Immunoblot detection and quantification of ARC/ARG3.1 in cerebellar homogenates from Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 5–6 mice per group). *P < 0.05 versus control. (E) ARC/ARG3.1 immunostaining in Cb1a6– and control mice. Plot represents ARC/ARG3.1 intensity along the cerebellar layers. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F) Motor coordination analysis of Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 11–15 per group). (G) Motor coordination analysis with the coat-hanger test in Cb1a6– and control mice (n = 8–10 per group). Four hours before the test, the mice received an injection of IL-1RA (100 mg/kg, i.p.) or its VEH (DMSO). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control. #P < 0.05 versus Cb1a6– plus DMSO.