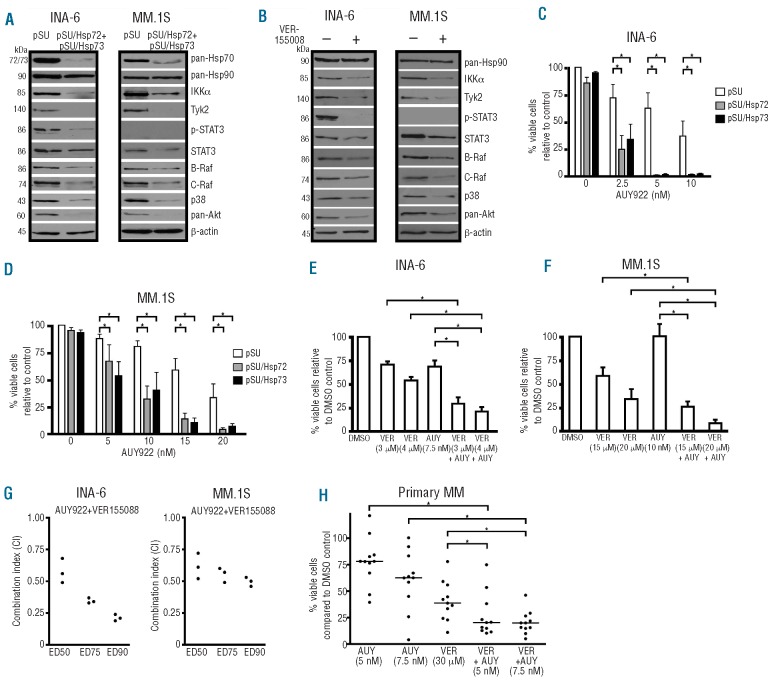
Figure 3.
Inhibition of Hsp72 and Hsp73 by siRNA-mediated knockdown or pharmacologically with VER-155008 leads to degradation of Hsp90-chaperone client proteins and enhances apoptosis induced by the Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 in MM cells. (A and B) Western blot analyses of Hsp90 client proteins 48 h post-transfection with siRNA against Hsp72 and Hsp73 (A) or after 24 h treatment with the Hsp70 inhibitor VER-155008 (15 μM) (B). Exemplary β-actin staining is shown as a loading control. (C-H) Experiments with combined inhibition of Hsp70/Hsp90 in MM cells are shown. (C and D) Hsp72/Hsp73 knockdown in INA-6 or MM.1S cells combined with the Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922. The drug was added 36 h post-transfection to purified transfected cells and cell death was determined after another 24 h by annex-in V/PI staining. Means and standard deviations are based on five independent experiments. (E and F) Concomitant treatment with VER-155008 and NVP-AUY922 for either 3 (INA-6) or 4 days (MM.1S) prior to cell death assessment with annexin V/PI (three independent experiments). (G) Combination analyses (three independent experiments) for NVP-AUY922 and VER-155008 with the combination index (CI) determined according to the method of Chou (fixed ratio design, simultaneous drug addition, 3 days of drug treatment). Results obtained for three different effect levels are shown. (H) Primary samples from 11 MM patients in co-culture with BMSC were treated for 3 days with either NVP-AUY922, VER-155008 or a combination of both. Viability was assessed by annexin V-FITC/PI and calculated with respect to the cognate DMSO controls. Where indicated (*), there was a significant (P<0.05) reduction in viability induced by the combination treatments.