FIGURE 8.
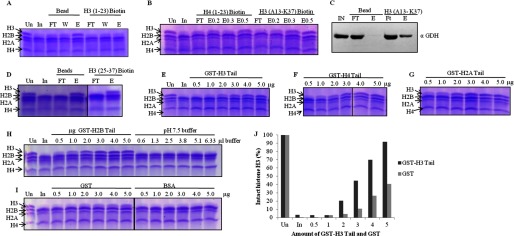
GDH interacts with all the core histones but clips only H3. In all gel pictures, lanes marked Un have undigested chicken brain core histones for reference. In is brain core histones digested by input, which is GDH active fraction. A, GDH pulldown by biotin-modified H3 (1–23) peptide conjugated to avidin beads using unmodified beads as control was fractionates into flow-through (FT), wash (W), and elution (E) preparations, incubated with brain core histones, and analyzed for H3-clipping activity on 15% SDS-PAGE. B, shown is a clipping assay from the fractions of peptide pulldown of GDH with biotin-labeled H3 (13–37) peptide and H4 (1–23) peptide. E0.2, E0.3, and E0.5 denote elutions in the presence of 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5 m NaCl. C, immunoblot analysis determines the presence of GDH in the peptide pulldown fractions using H3 (13–37) peptide. D, shown is a clipping assay from the fractions of peptide pulldown of GDH with H3 (25–37) peptide. E–H, shown is competitive inhibition of GDH by GST-histone tails. GST-tagged tails of histone H3 (residues 1–41) (E), histone H4 (residues 1–36) (F), histone H2A (residues 1–38) (G), and histone H2B (residues 1–33) (first six lanes of panel H) were used. Increasing amounts of GST-tagged tails were added to the brain core histones and GDH in assay buffer, incubated at 37 °C for 1 h, and then resolved on 15% SDS-PAGE. The control experiments were performed by using increasing amounts of pH 7.5 buffer (last six lanes of panel H) in the reaction mixtures (instead of GST-histone tails) to verify that the inhibition was not caused by higher pH. Protease assay in the presence of pure GST and BSA proteins (I) served as controls. J, shown is quantification of protease activity inhibition due to GST-H3 tails as compared with same due to GST.
