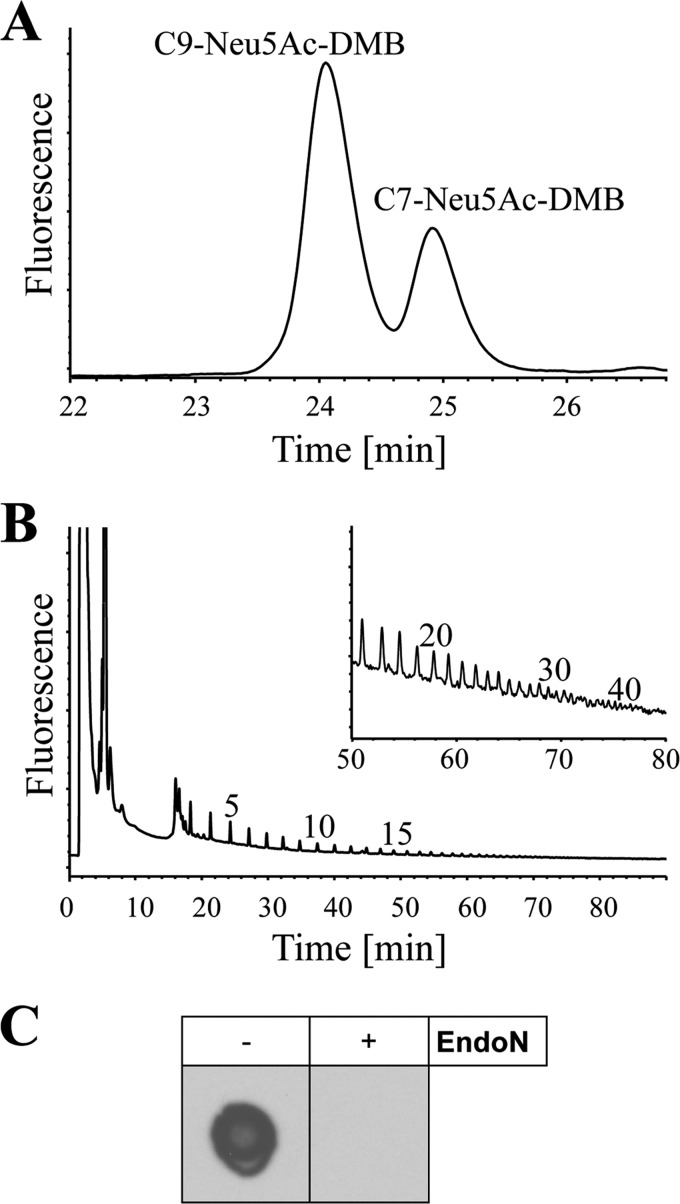
FIGURE 1.
Detection of polySia in human semen. A, terminal and internal sialic acid residues of the protein fraction of human semen were visualized by the C7/C9 method. After subsequent metaperiodate oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, and DMB labeling, C7-Neu5Ac-DMB and C9-Neu5Ac-DMB were separated by reverse phase-HPLC. Internal sialic acid residues resulted in the detection of C9-Neu5Ac-DMB, whereas terminal ones are detected as C7-Neu5Ac-DMB. B, for characterization of the polySia chain length, protein fraction of the whole ejaculate was subjected to the mild DMB method. DMB-labeled sialic acid polymers were separated by anion exchange chromatography according to the chain length. Respective numbers of sialic acid residues are given for single peaks on top of the profiles. C, proteins were transferred to a PVDF membrane, and polySia was visualized with the mAb 735. For negative control polySia was degraded with endoN.