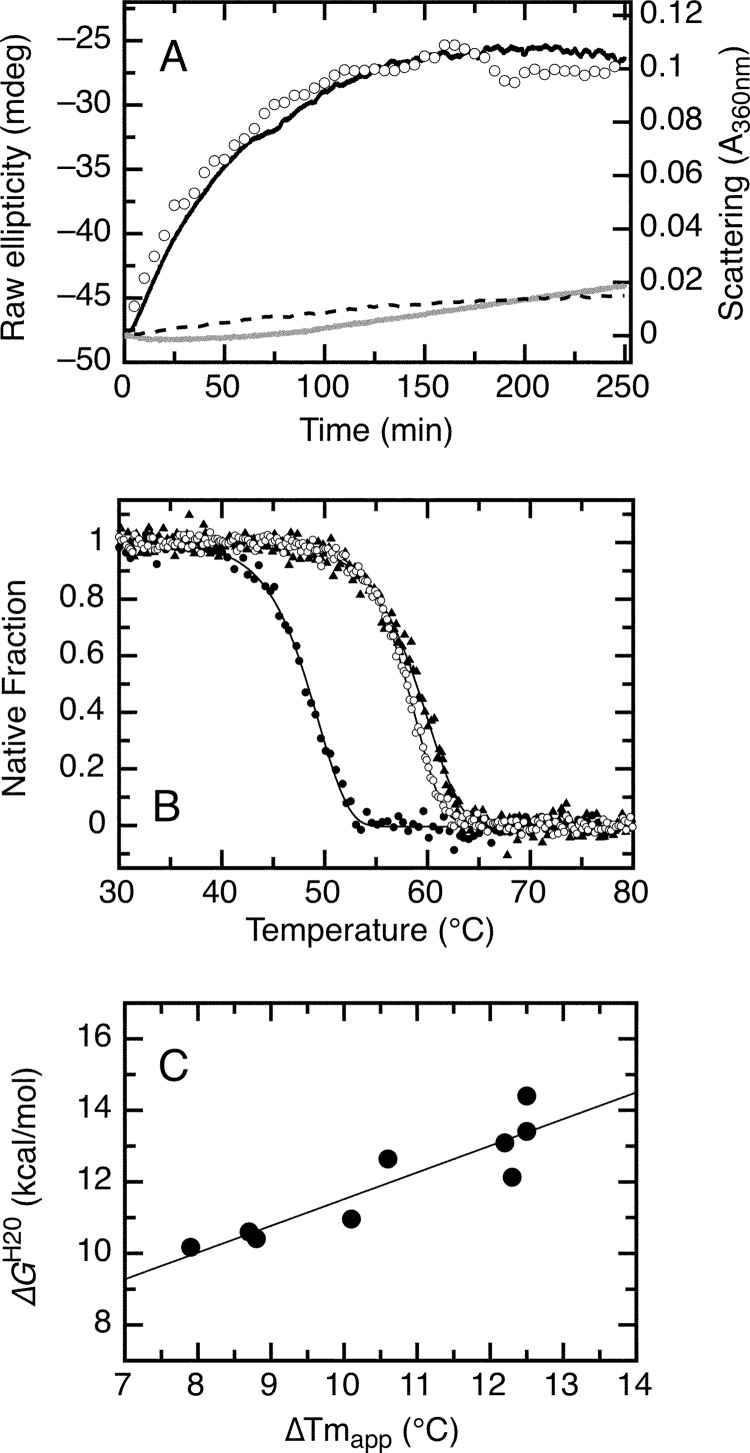
FIGURE 8.
Irreversible thermal denaturation of the RbAB domain at 37 °C and effect of LXCXE and E2F-TD peptide ligands on thermal stability. A, aggregation kinetics of the isolated RbAB domain at 37 °C and 5 μm concentration followed by light scattering (black line) and by far-UV CD (open circles) and aggregation kinetics of 5 μm RbAB in complex with 20 μm E7(16–31) peptide (dark gray line) or with 20 μm E2F-TD peptide (broken line) followed by light scattering. B, thermal scans of the isolated RbAB domain at 2 μm concentration (filled black circles; Tm(app) = 49.5 ± 0.1 °C) and of complexes of 2 μm RbAB domain with 20 μm E7(16–31) peptide (filled black triangles; Tm(app) = 60.1 ± 0.1 °C) or with 20 μm E2F-TD peptide (open black circles; Tm(app) = 58.9 ± 0.1 °C) (Table 2). Lines are fits to Equation 16. C, correlation between the binding free energy and the change in apparent melting temperature for a set of peptides containing the LXCXE motif (data are from Table 3). The line is a linear fit of the data (correlation coefficient r = 0.892). mdeg, millidegrees.