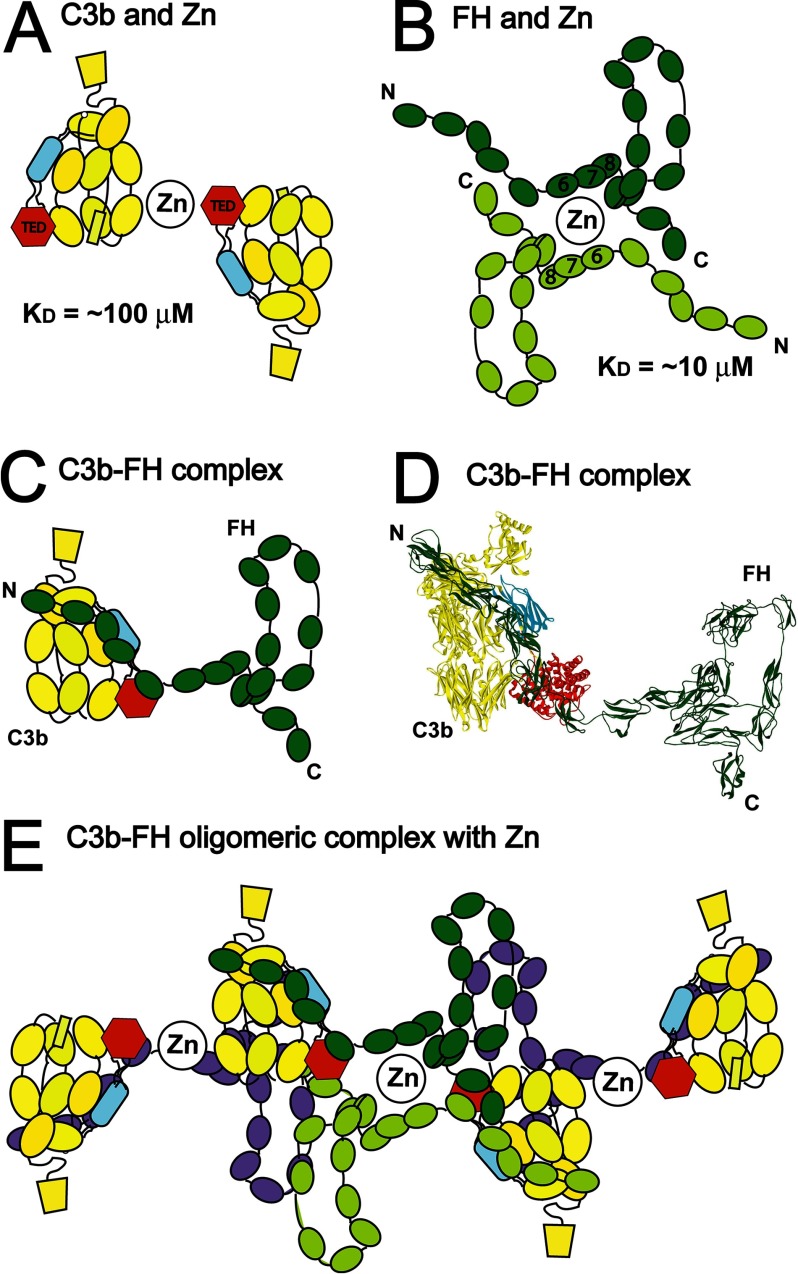
FIGURE 9.
Schematic outlines of the zinc-induced oligomerization of FH-zinc, C3b-zinc, and C3b-FH-zinc complexes. A, a putative C3b dimer is shown in which the C3c and C3d regions in yellow and red, respectively in two monomers are cross-linked by zinc. Other cross-linked forms of C3b can also be formed by the daisy-chaining of the cross-linking. B, a putative FH dimer is shown in which the SCR-6/8 domains are cross-linked by zinc. These structures can also be daisy chained to form larger oligomers. C and D, the crystal structure of C3b with SCR-1/4 of FH is shown as a schematics form and as a molecular structure (PDB code 2WII) to which SCR-5/20 from the folded-back solution structure of FH SCR-1/20 (PDB code 3GAV; R. Nan, unpublished modeling) is added to indicate their interaction. C3b is shown in yellow (with the CUB domain in blue and the TED domain in red) and FH is shown in green. E, the formation of large aggregates of C3b-FH-zinc is shown. The daisy-chaining of the two dimers shown in A and B is accompanied by the formation of the C3b-FH complex to form an aggregated particle. Further FH monomers (in purple) are able to bind to the two C3b dimers, and these purple FH monomers are also able to bind zinc and dimerize further.