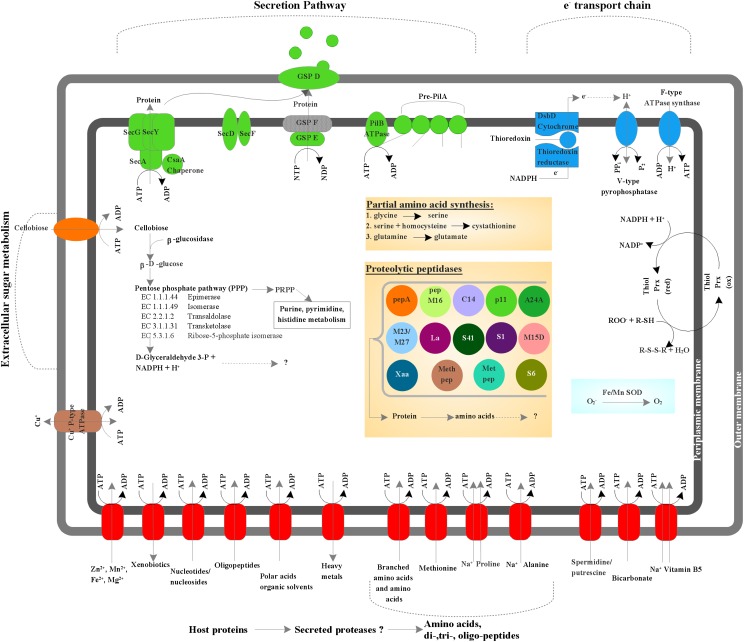
Fig. 5.
Predicted metabolic pathways of phylotype TM6SC1. Predicted ABC transporters (e.g., amino acid importers, nucleotide/nucleoside importers, divalent ion importers) (red) as well as a cellobiose importer (orange). ATP-driven transporters are indicated by the ATP hydrolysis reaction. The copper ion transporting P-type ATPase is proposed to serve as both uptake and efflux systems, which is shown by a bidirectional arrow. Several protein-secretion components belonging to the type II secretion pathway; GSP and Sec proteins were identified as well as five prepilin related domains and a type IV pilB ATPase (green). A modified electron transport chain was also identified consisting of seven thioredoxins and five thioredoxin reductases, a V-type pyrophosphatase, an F-type ATPase synthase, and a protein disulfide reductase (DsbD) (blue). Thiolperoxidases (Bcp and bacterioferretine-like), superoxide dismutases (manganese and iron), were identified as cytosolic and periplasmic enzymes protecting against oxidative stress. A β-glucosidase that catalyzes the formation of β-d-glucose from disaccharides (e.g., cellobiose) was identified as well as all enzymes involved in the pentose phosphate pathway. However, other enzymes (e.g., enzymes from the Calvin cycle or the citric acid cycle) involved in the conversion of 3-glyceraldehyde-3-P could not be identified. Enzymes for de novo synthesis of amino acids were absent, however several amino acid importing membrane proteins (ABC transporters), and 14 cytosolic and proteolytic peptidases were identified, indicating that TM6 has a high capacity for amino acid scavenging.