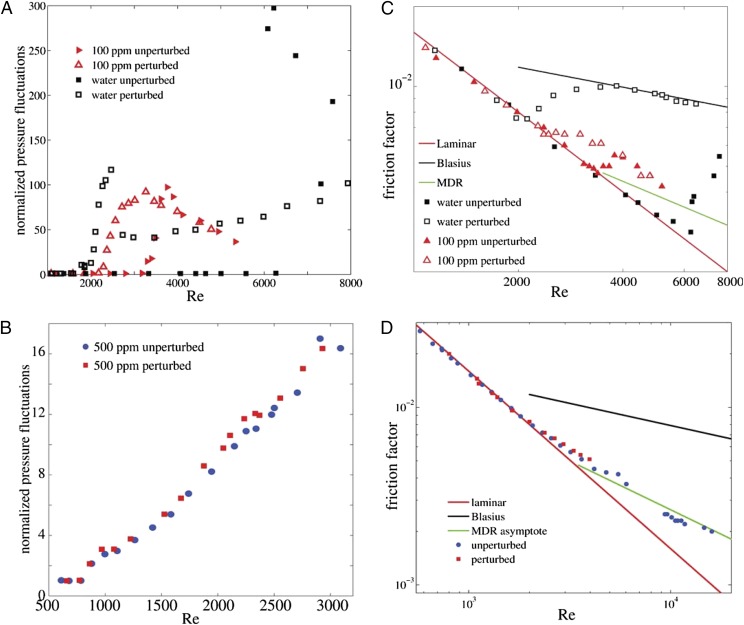
Fig. 2.
Stability and friction scaling. (A) For the Newtonian case (black symbols), turbulence can first be triggered by perturbations for 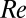 of about 2,000, where fluctuations increase rapidly. The quantity plotted is the fluctuation in pressure that was measured differentially between two pressure taps (1-mm holes in the pipe wall) separated by
of about 2,000, where fluctuations increase rapidly. The quantity plotted is the fluctuation in pressure that was measured differentially between two pressure taps (1-mm holes in the pipe wall) separated by 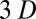 in the streamwise direction and located approximately
in the streamwise direction and located approximately 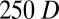 from the pipe exit. (B) For a 100-ppm polymer solution (red data points), turbulence cannot be triggered below
from the pipe exit. (B) For a 100-ppm polymer solution (red data points), turbulence cannot be triggered below 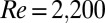 (transition delay). At
(transition delay). At  , however, instability occurs (even in the absence of perturbations), and this instability is caused solely by the presence of the polymers. At higher polymer concentrations (B; 500 ppm here), this instability occurs at a much lower
, however, instability occurs (even in the absence of perturbations), and this instability is caused solely by the presence of the polymers. At higher polymer concentrations (B; 500 ppm here), this instability occurs at a much lower 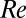 and the hysteresis typical for Newtonian turbulence has disappeared (A and C). The flow already becomes unstable at
and the hysteresis typical for Newtonian turbulence has disappeared (A and C). The flow already becomes unstable at 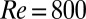 (regardless of the presence of additional perturbations). From here (with an increasing
(regardless of the presence of additional perturbations). From here (with an increasing 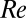 ), the flow directly approaches the MDR friction scaling (D; also for a concentration of 500 ppm).
), the flow directly approaches the MDR friction scaling (D; also for a concentration of 500 ppm).