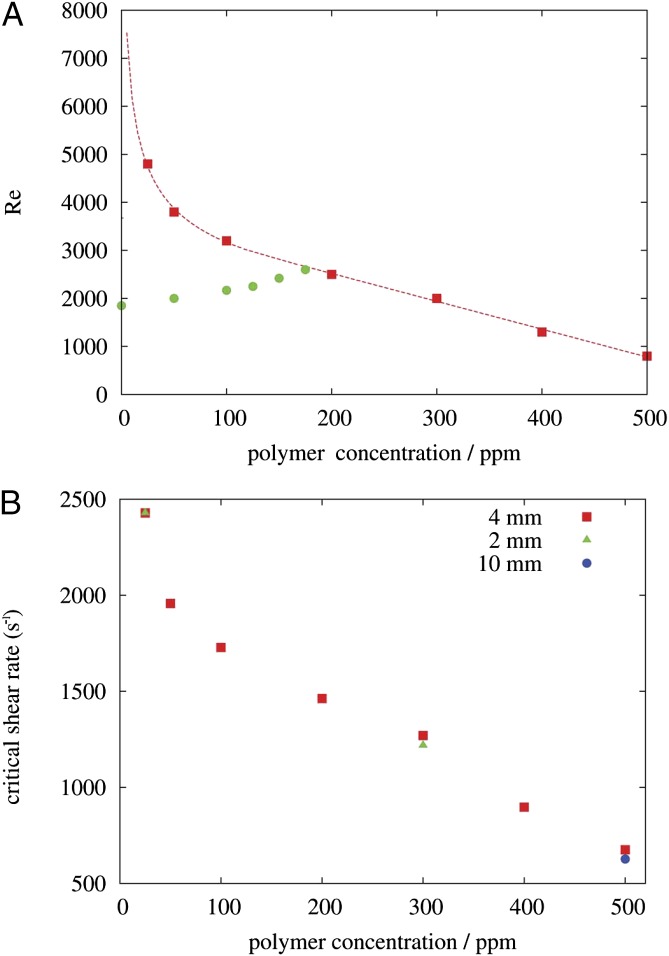
Fig. 3.
Transition threshold to EIT is plotted for different concentrations (red squares). The red line is a guide for the eye. The green circles mark the transition delay to ordinary turbulence (Fig. 1B). Consequently, for concentrations below 200 ppm, the elasto-inertial instability sets in at a 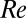 at which ordinary turbulence can already occur, whereas in the
at which ordinary turbulence can already occur, whereas in the 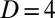 -mm pipe, the elasto-inertial instability is found only above 200 ppm. (B) Red squares mark the critical shear rate for the onset of EIT in the 4-mm pipe (same as red squares in A). In addition, shear rates (
-mm pipe, the elasto-inertial instability is found only above 200 ppm. (B) Red squares mark the critical shear rate for the onset of EIT in the 4-mm pipe (same as red squares in A). In addition, shear rates (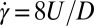 ) were determined for the flow in a
) were determined for the flow in a 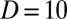 -mm pipe and a
-mm pipe and a 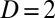 -mm pipe. In these cases, the transition occurs at the same critical shear rate. Hence, unlike ordinary turbulence, the onset of EIT is not governed by the
-mm pipe. In these cases, the transition occurs at the same critical shear rate. Hence, unlike ordinary turbulence, the onset of EIT is not governed by the 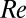 but, instead, by the shear rate.
but, instead, by the shear rate.