Fig. 5.
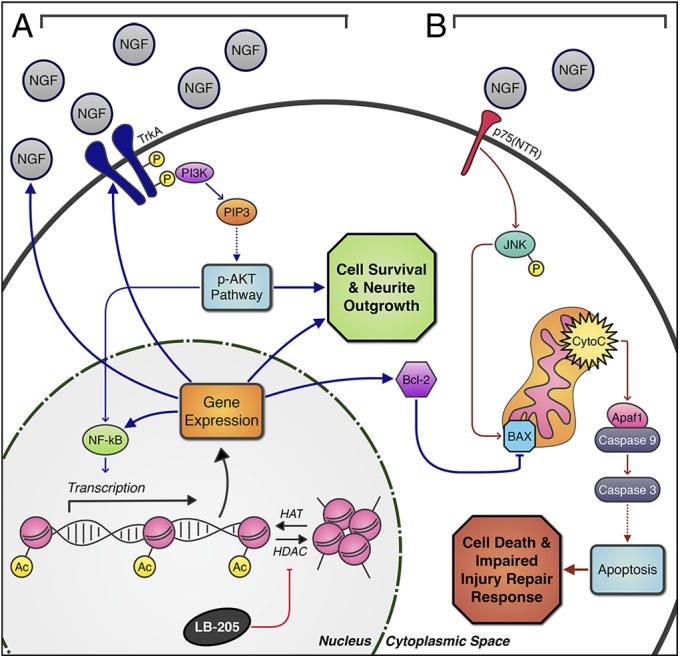
Schematic depiction of LB-205 effects on NGF stimulated pathways. (A) LB-205 inhibits HDACs and increases acetylation of histones by histone acetyltransferases (HATs), which play a key role in regulating gene expression in the nucleus. Activated PI3K initiates the p-AKT pathway, which acts through NF-κB transcriptional modification and other targets to alter expression of NGF, TrkA, and NF-κB to promote cell survival, growth, and proliferation. In addition, BAX is blocked through increased Bcl-2 expression, inhibiting the apoptosis pathway. (B) Without LB-205 treatment, decreased NGF and increased p75(NTR) expression post-TBI induce p-JNK through the p75(NTR) receptor-mediated pathway and subsequent release of apoptosis associated factors from the mitochondria, triggering the caspase cascade through BAX activation, inducing cell apoptosis, and impairing the CNS injury repair response.
