Fig. 4.
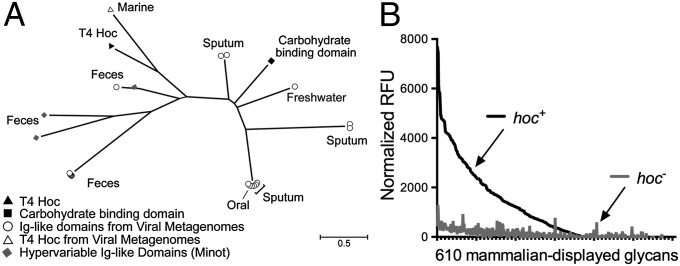
Hoc-mediated glycan binding and Hoc-related phylogeny. (A) Phylogenetic tree of sequences from viral metagenomes with high-sequence homology to Ig-like domains. Many of the identified homologs are from mucus-associated environments (e.g., human feces, sputum). Also included are the Hoc protein of T4 phage and the hypervariable Ig-like domains previously obtained by deep sequencing of phage DNA from the human gut (44). The scale bar represents an estimated 0.5 amino acid substitutions per site. See SI Materials and Methods for methods. (B) Binding of fluorescence-stained hoc+ and hoc– T4 phage to a microarray of 610 mammalian glycans. Normalized relative fluorescence units (RFU) were calculated from mean fluorescence minus background binding.
