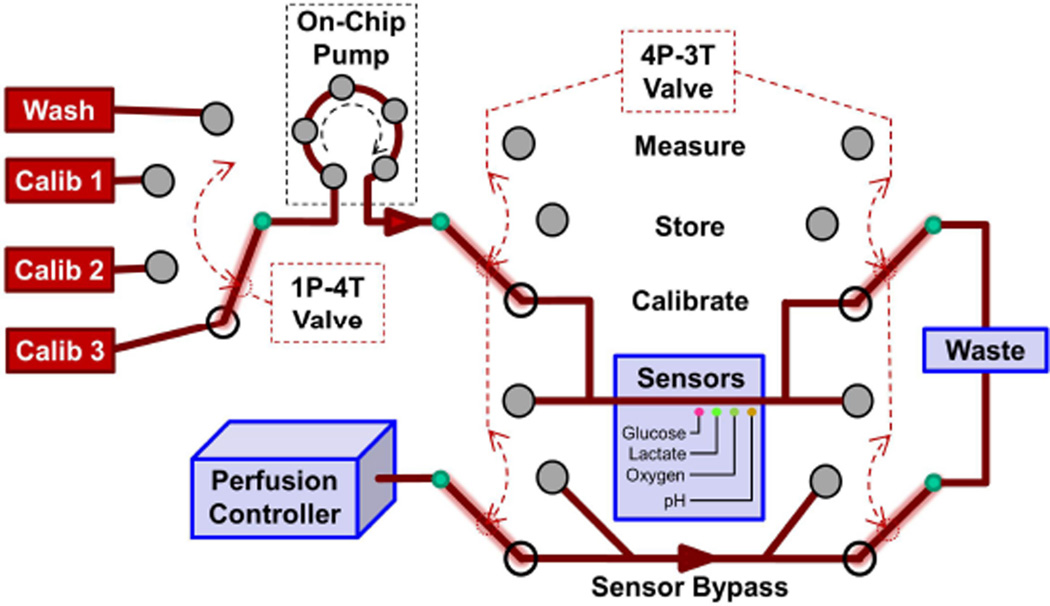
Fig. 6.
Conceptual drawing of how 1P-4 T and 4P-3 T valves and another on-chip peristaltic pump could provide the requisite µCA functions in Fig. 2. The valve configuration shown would allow calibration of the electrochemical sensor array with one of three standard solutions (configuration shown) or sensor washing without affecting the organ. Other modes allow the organ effluent to bypass the washed sensor to minimize biofouling (Store), or the delivery of organ fluid to the calibrated electrochemical sensor array (Measure). In this design, all of the µCA output is sent to waste rather than to venous return.