Figure 1.
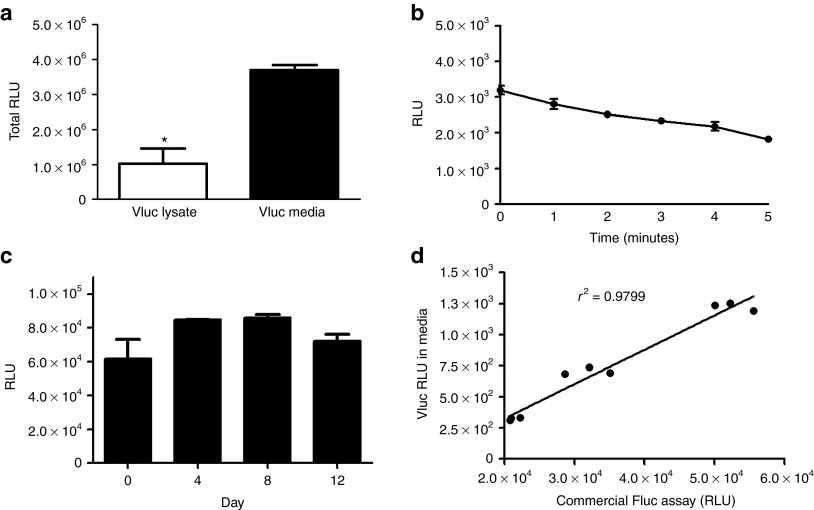
In vitro characterization of Vluc-catalyzed luminescence. (a) Vluc assay was performed on conditioned medium as well as cell lysates from 293T cells transduced with a lentivirus vector encoding Vluc to determine the fraction (in RLU) of Vluc being secreted (n = 3; *P = 0.003). (b) Vluc light emission kinetics was performed by adding the vargulin substrate to Vluc-containing media (n = 3). (c) Stability of Vluc enzyme was determined by assaying an aliquot of Vluc-containing cell-free conditioned medium, incubated at 37 °C, at different time points (n = 3). The slight increase observed between day 0 and 4 is not statistically significant (P = 0.176). (d) Vluc-based viability assay. 105 U87 cells expressing Vluc were seeded in 12-well plates and an aliquot of conditioned medium was assayed for Vluc activity over time. For comparison, a commercially available Fluc-based viability assay was performed on the same cells from which Vluc-media was isolated (n = 3 per time point). RLU, relative light unit.