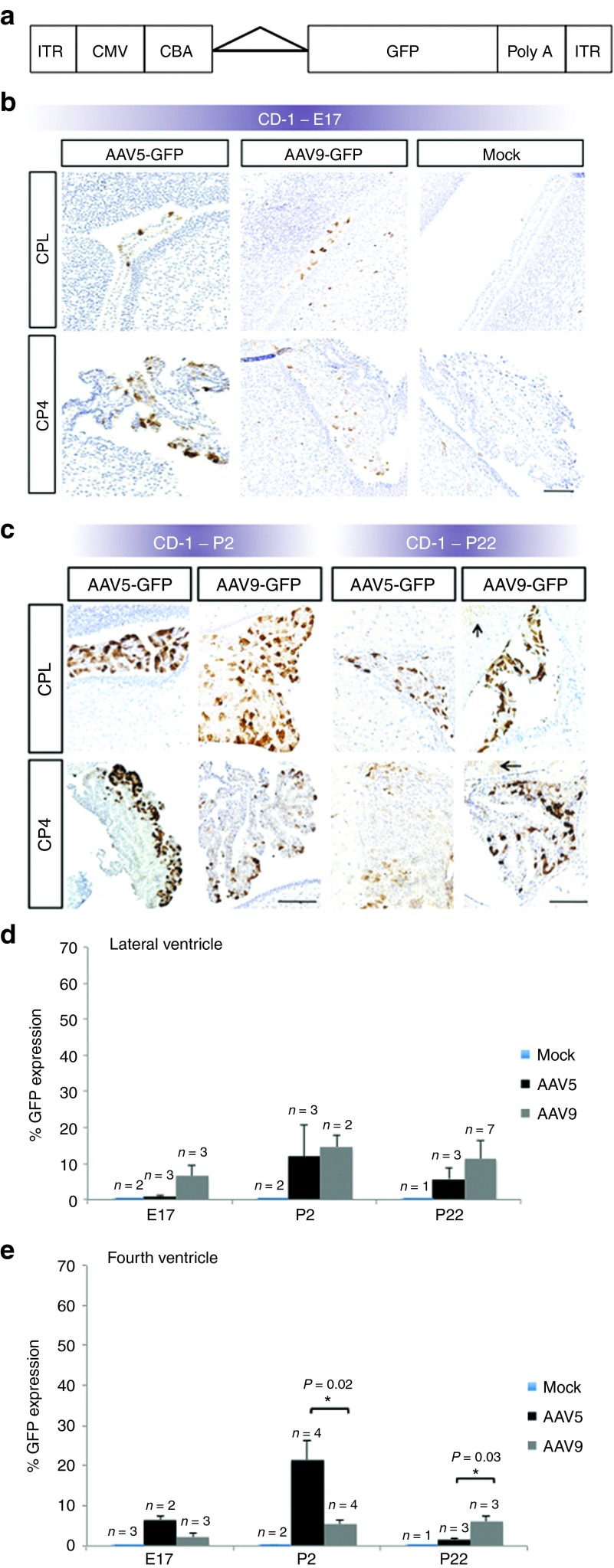
Figure 2.
Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV)-mediated gene expression in CD-1 fetal mouse choroid plexus. (a) Elements of the rAAV construct. Flanked by inverted terminal repeat (ITR) motifs, the rAAV construct includes a cytomegalovirus (CMV) enhancer, chicken β-actin (CBA) promoter, intronic sequence (triangle), complementary DNA (cDNA) for green fluorescent protein (GFP), and a poly-adenylation (poly-A) tail. (b) Representative immunohistochemistry images of GFP transgene expression at E17 in CD-1 mouse brains, after rAAV serotype 5 or 9, or mock injection on E15. (c) Representative images of P2 and P22 CD-1 mouse brains after rAAV serotype 5 or 9, or mock injection on E15. Brown stain indicates GFP expression. Arrows indicate AAV9-GFP–mediated expression in adjacent brain parenchyma on P22. CPL: choroid plexus-lateral ventricle; CP4: choroid plexus-fourth ventricle. Bars, 100 μm. Of the three timepoints evaluated, densitometric quantitation showed peak transgene expression on P2 in the (d) lateral and (e) fourth cerebral ventricles. Statistically significant differences between rAAV5- and rAAV9-mediated GFP expression were evident only in the fourth ventricle choroid plexus epithelia, as shown.