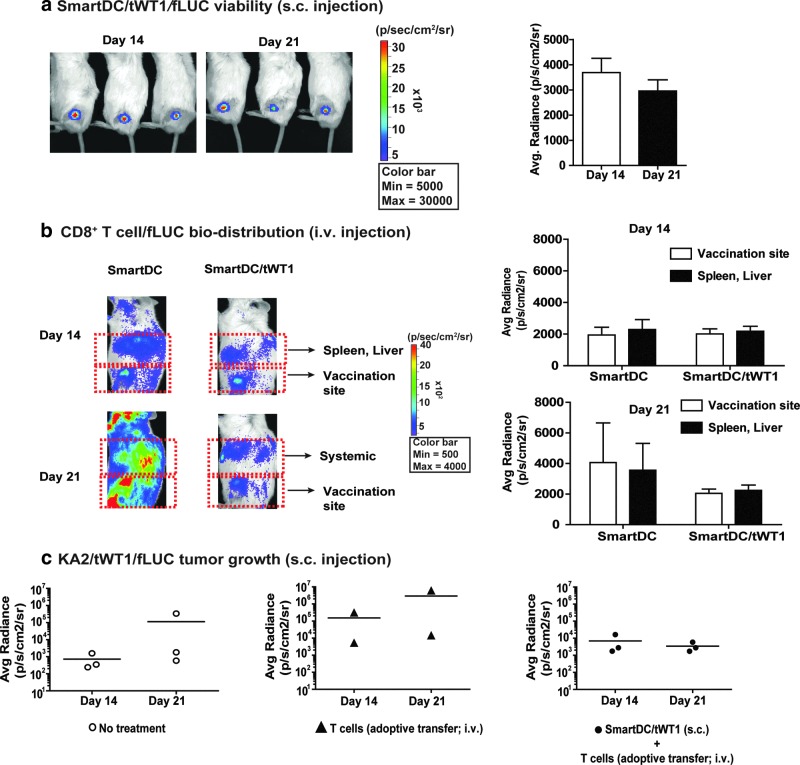
FIG. 7.
Viability and potency of SmartDC/tWT1 in vivo. (a) Viability: SmartDC/tWT1/fLUC (5×105 cells) were injected s.c. into the hind flanks of NRG mice and in vivo optical imaging analyses were performed on days 14 and 21 post injection. The reference color bar indicates high bioluminescence signals in red and low signals in blue. The bioluminescence signal emitted at the injection site was quantified and is depicted as average of radiance (n=3). Error bars indicate standard error of mean (SEM). (b) T-cell biodistribution: SmartDC/tWT1 (5×105 cells) were injected s.c. into the hind flanks of NRG mice and CD8+ T cells/fLUC were injected seven days later i.v. In vivo optical imaging analyses were performed 14 and 21 days after T-cell infusion for biodistribution analyses at the injection site versus systemic biodistribution (spleen and liver). The bioluminescence signals were quantified and are represented as average per group (n=3). (c) Protection against KA2/WT1/fLUC tumor growth. KA2/tWT1/fLUC (5×105 cells) and SmartDC/tWT1 (5×105 cells) were injected s.c. into the right and left hind flanks of NRG mice, respectively. Seven days later, T cells expanded in vitro with SmartDC/tWT1 (2×106 cells) were infused into mice immunized with SmartDC/tWT1. Tumor growth was monitored by optical imaging analyses 14 and 21 days after T-cell infusion. Bioluminescence signal, depicting the growth of the KA2/tWT1/fLUC, was quantified and depicted as scatter graph per group (n=3).