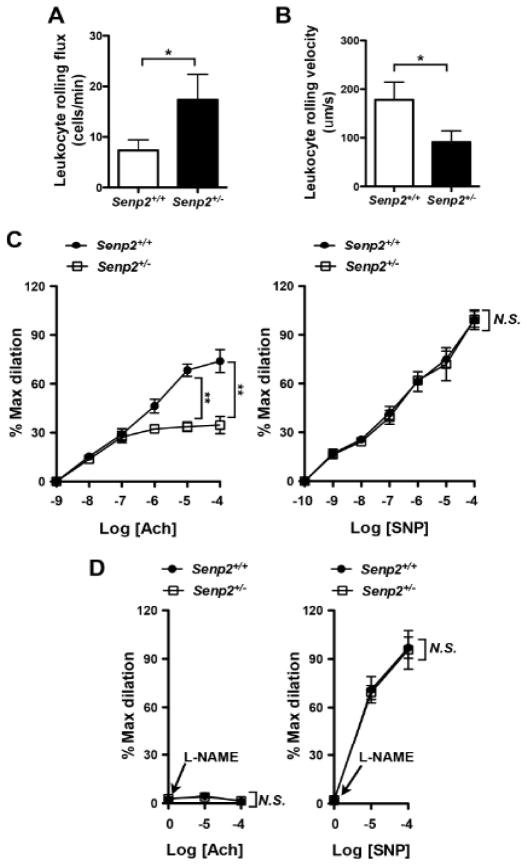
Figure 7. Increased leukocyte rolling and reduced endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in Senp2+/− mice.
Leukocyte rolling in vivo. Quantified data on leukocyte rolling flux (A) and leukocyte rolling velocity (B) are shown. To analyze these parameters, image analysis software (NIS elements, Nikon) was used (n = 4, mean ± S.D.; **, P < 0.01). (C) Endothelium-dependent vessel relaxation by ACh (left) was inhibited, while SNP (right)-induced relaxation did not show any differences between Senp2+/− and Senp2+/+ arterioles. At least, two arterioles per animals were examined. Data are shown as the mean ± S.D., n = 4 mice, **P < 0.01. (D) Effect of L-NAME on the ACh (left)- or SNP (right)-induced vessel dilation in arterioles of Senp2+/+ and Senp2+/− mice. Data are shown as the mean ± S.D., n = 4 mice, **P < 0.01. Not significant, N.S.