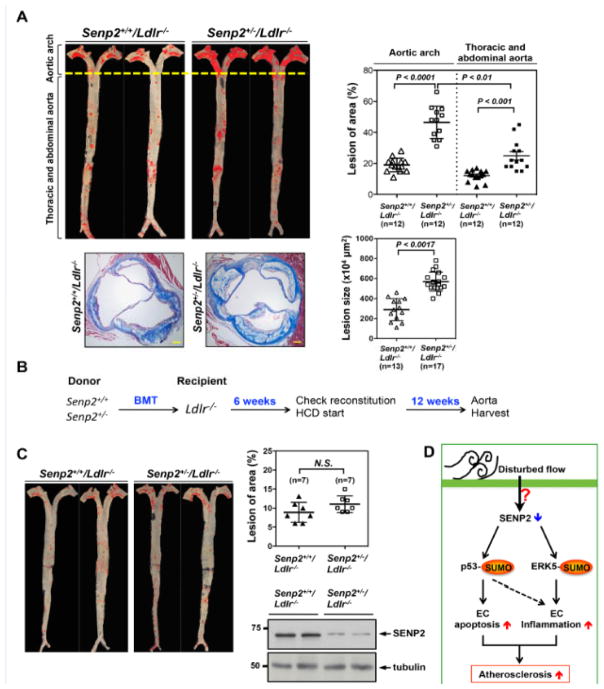
Figure 8. Reduced SENP2 expression accelerates atherosclerotic plaque formation, which is mediated by vascular but not by hematopoietic cells.
Senp2+/+/Ldlr−/− and Senp2+/−/Ldlr−/− mice were given a high cholesterol diet for 16-week. Senp2+/−/Ldlr−/− mice exhibited increased Oil red O-stained atherosclerotic lesions in the whole aorta, (top, left) as well as, increased Masson’s trichrome stained atherosclerotic lesions in the cross-section of aortic valve region (bottom, left two). Bars, 50 μm. The graphs on the right show quantification of these data. Mean ± S.D. (n=12, whole aorta of Senp2+/+/Ldlr−/− and Senp2+/−/Ldlr−/−; n=13, Senp2+/+/Ldlr−/−; and n=17, Senp2+/−/Ldlr−/−). The lesions of aortic arch compared to the lesion of descending aorta in the Senp2+/−/Ldlr−/− mice are shown. **P<0.01. (B) The scheme of bone marrow transplantation. The transplantation of bone marrow cells from Senp2+/+ or Senp2+/− mice into Ldlr−/− mice was performed and 6-week later, mice were given a high cholesterol diet for 12-week. (C) Atherosclerotic lesions were identified by Oil red O staining of the whole aorta (C, left). The graphs show quantified data (C, right upper). Mean ± S.D. (n=7). Not significant, N.S. The successful chimerism of BM cells was confirmed by Western blotting with anti-SENP2 using the blood cells after 6-weeks transplantation (C, right lower). (D) Schematic diagram showing the p53 and ERK5 SUMOylation signaling pathway mediating the EC apoptosis and inflammation to cause the atherosclerosis formation in response to disturbed flow.