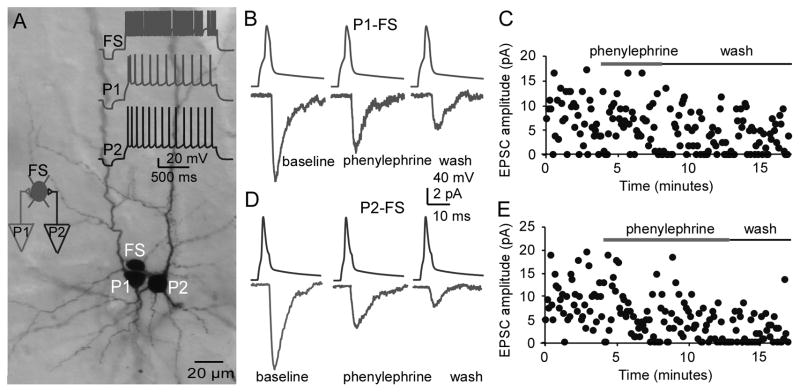
Figure 7.
Phenylephrine inhibits excitatory transmissions in a triple connection in which two pyramidal neurons innervated the same FS interneurons. A, Photomicrograph of the biocytin-labeled pyramidal neurons and FS interneuron. The firing patterns of these three neurons are shown in the inset of A. In this converging connection, the membrane potential of the FS interneuron was held at −70 mV, and the EPSCs in the P1-FS connection were first recorded in the presence of phenylephrine. After washout, the EPSCs in the P2-FS connection were subsequently recorded and phenylephrine was reapplied. B and C, The sample traces and scatter plot showing the AMPA EPSCs in the P1-FS connection, which was clearly inhibited by the alpha-1 agonist phenylephrine (25 μM). D and E, The sample traces and scatter plot of the AMPA EPSCs in the P2-FS connection that were similarly inhibited by phenylephrine. These data further verified the results shown in Figure 6.