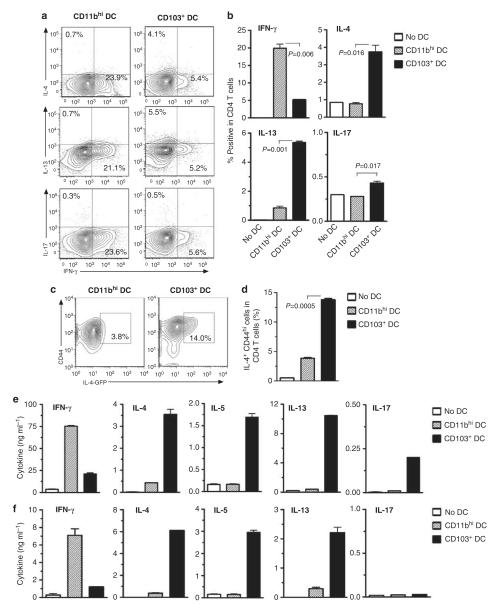
Figure 2.
CD103+ dendritic cells (DCs) promote Th2 differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells. (a, b) DCs prepared from the lungs of C57BL/6 mice treated with ovalbumin together with lipopolysaccharide (OVA-LPS) were cocultured with naive CD4+ T cells from rag-2−/− OT-II mice. Intracellular cytokines in CD4+ T cells were analyzed after 6 days of coculture. Percent of cytokine positive CD4 T cells are indicated in contour plots (a) and histograms of compiled data (b). Data shown represent one of three similar experiments; P-values by Student’s t-test. (c, d) DCs prepared from the lungs of BALB/c mice treated with OVA-LPS were cocultured with naive CD4+ T cells from interleukin (IL)-4-green fluorescent protein (GFP) DO11.10 mice. Percentage of IL-4-GFP+ CD44hi cells among all CD4+ T cells after 5 days of coculture are indicated in contour plots (c) and histograms of compiled data (d). (e, f) Cytokine production by DC-stimulated T cells. The indicated lung DC subsets were prepared from the lungs or mediastinal lymph nodes (f) of OVA-LPS-treated mice and cocultured for 5 days with naive Rag2−/− OT-II CD4+ T cells. Cultured T cells were incubated for 24 h in anti-CD3ε and anti-CD28-coated plates. Cytokines in the supernatants were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Data presented represent one of at least three independent experiments yielding similar results. IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL, interleukin.