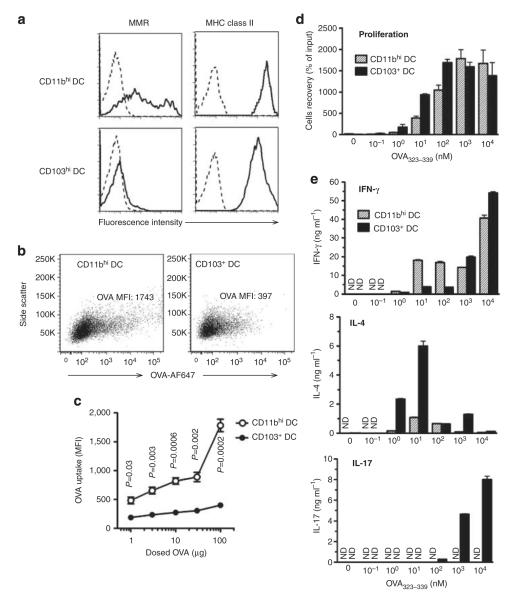
Figure 6.
Effect of antigen uptake by lung dendritic cell (DC) subsets on T-cell differentiation. (a) Surface molecule display. Macrophage mannose receptor (MMR) and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II on lung DC subsets of untreated C57BL/6 mice were stained with specific antibodies (solid line) or with isotype control antibodies (dotted line). (b) Ovalbumin (OVA) uptake by DC subsets. Flow plots are shown for OVA-Alexa Fluor (AF)-647 fluorescence in CD11bhi and CD103+ lung-resident DCs at 24 h after instillation of 100 μg OVA-AF647 together with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). (c) OVA-AF647 uptake (mean fluorescence intensity, MFI) by the lung-resident DCs after instillation of various amounts of OVA-AF647. P-value by Student’s t-test (n=3). Results from one of the two similar experiments are shown. (d, e) Effect of peptide concentration on T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. CD11bhi and CD103+ lung-resident DCs were prepared from lungs of untreated C57BL/6 mice, loaded with the indicated amounts of OVA323–329 peptide ex vivo, and cultured with naive CD4+ OT-II T cells. Proliferation of T cells in cocultures (d) and cytokine production from T cells measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay following elicitation by anti-CD3ε and CD28 antibodies (e) are indicated. One of the two independent experiments yielding similar results is shown. IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; ND, not detected.