Abstract
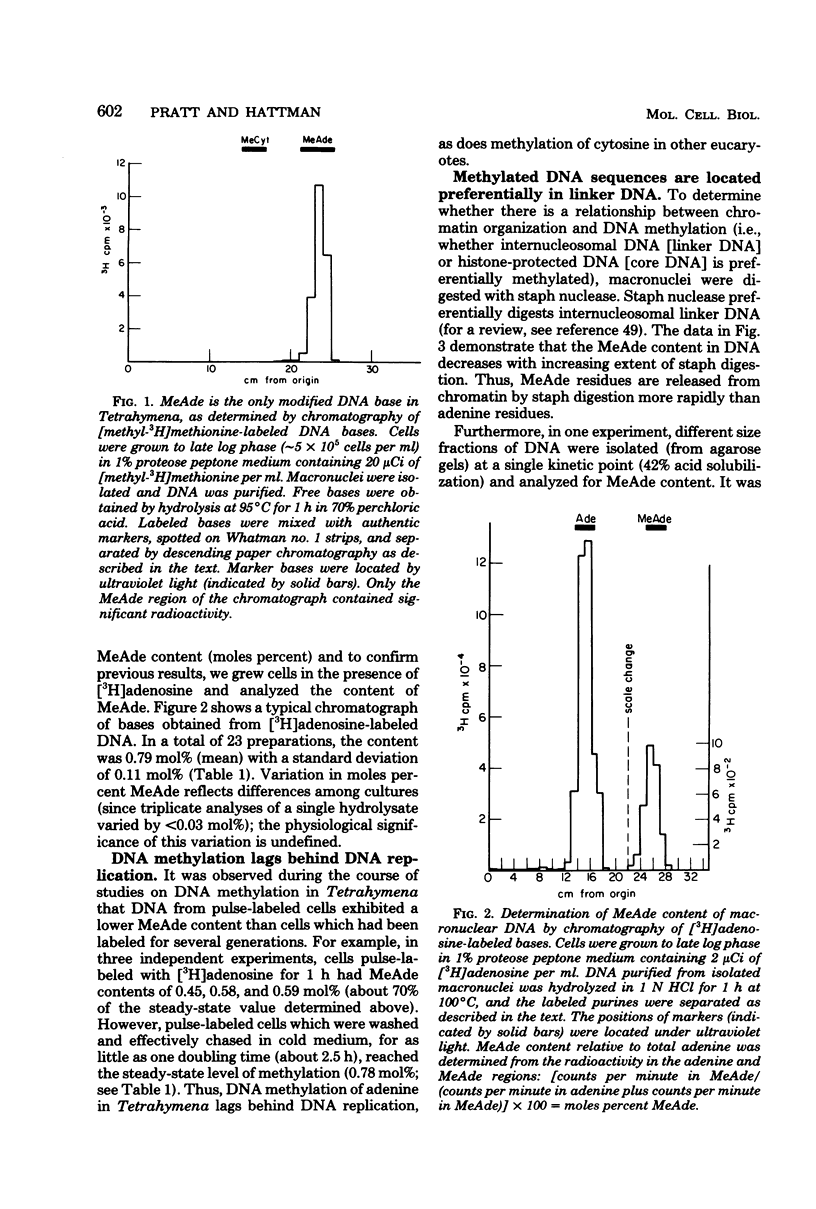
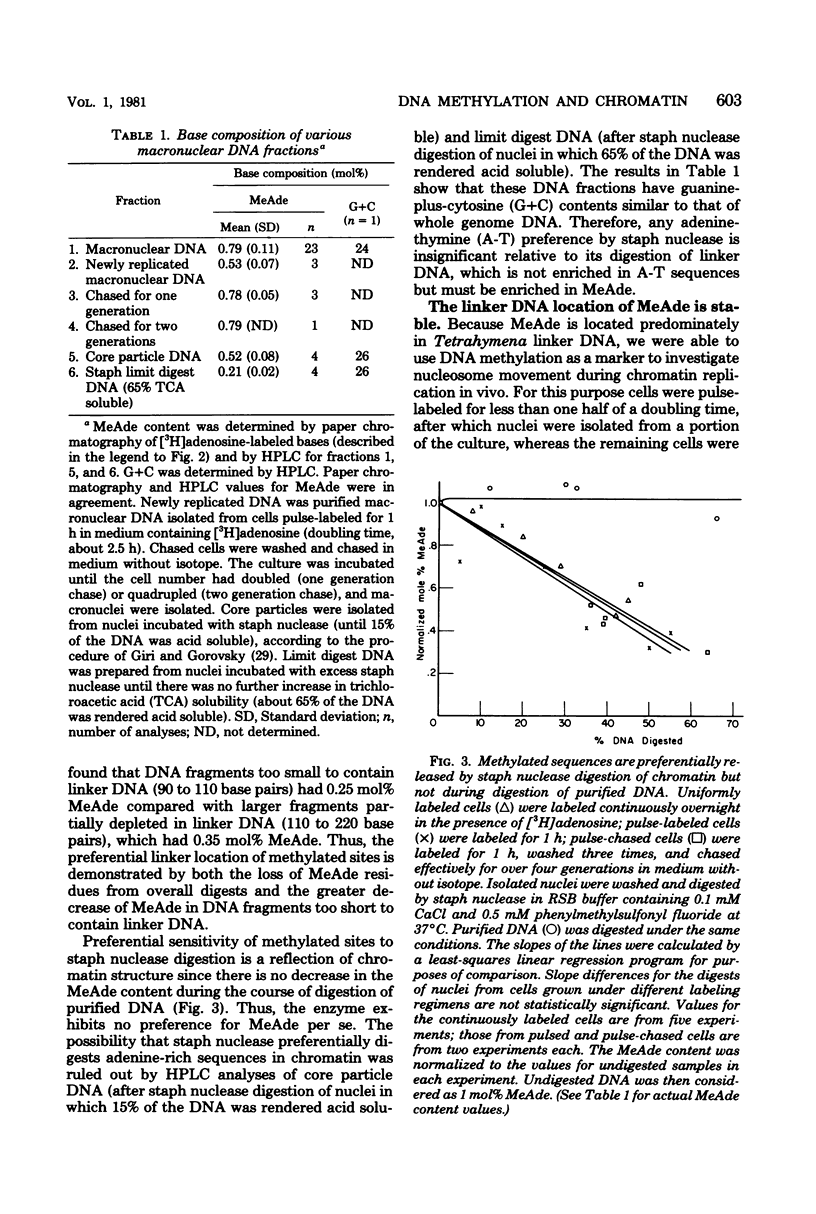
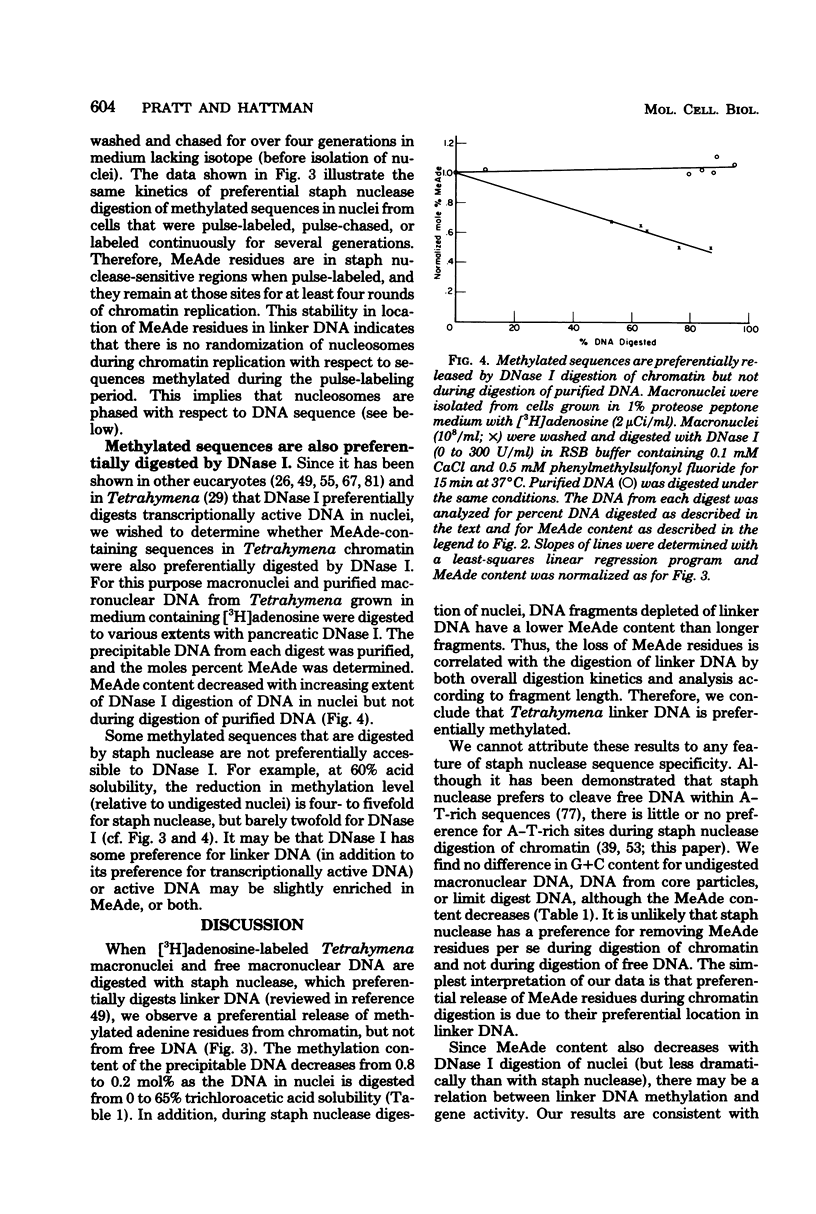
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the transcriptionally active macronucleus of Tetrahymena thermophila is methylated at the N6 position of adenine to produce methyladenine (MeAde); approximately 1 in every 125 adenine residues (0.8 mol%) is methylated. Transcriptionally inert micronuclear DNA is not methylated (< or = 0.01 mol% MeAde; M. A. Gorovsky, S. Hattman, and G. L. Pleger, J. Cell Biol. 56:697-701, 1973). There is no detectable cytosine methylation in macronuclei in Tetrahymena DNA (< or = 0.01 mol% 5-methylcytosine). MeAde-containing DNA sequences in macronuclei are preferentially digested by both staphylococcal nuclease and pancreatic deoxyribonuclease I. In contrast, there is no preferential release of MeAde during digestion of purified DNA. These results indicate that MeAde residues are predominantly located in "linker DNA" and perhaps have a function in transcription. Pulse-chase studies showed that labeled MeAde remains preferentially in linker DNA during subsequent rounds of DNA replication; i.e., there is little, if any, movement of nucleosomes during chromatin replication. This implies that nucleosomes may be phased with respect to DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams R. L., Hogarth C. DNA methylation in isolated nuclei: old and new DNAs are methylated. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 7;331(2):214–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90434-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L., McKay E. L., Craig L. M., Burdon R. H. Methylation of mosquito DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 20;563(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams R. L., McKay E. L., Douglas J. T., Burdon R. H. Methylation of nucleosomal and nuclease sensitive DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Sep;4(9):3097–3108. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.9.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakayev V. V., Schmatchenko V. V., Georgiev G. P. Subnucleosome particles containing high mobility group proteins HMG-E and HMG-G originate from transcriptionally active chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1525–1540. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Gannon F., Chambon P. Nucleosome structure III: the structure and transcriptional activity of the chromatin containing the ovalbumin and globin genes in chick oviduct nuclei. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):779–791. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Kuo M. T., Dretzen G., Chambon P. Differential nuclease sensitivity of the ovalbumin and beta-globin chromatin regions in erythrocytes and oviduct cells of laying hen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2737–2750. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 11;8(7):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.7.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Southern E. M. Use of restriction enzymes to study eukaryotic DNA methylation: I. The methylation pattern in ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 5;118(1):27–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch S., Cedar H. Methylation of chromatin DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Jun;3(6):1507–1519. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.6.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom K. S., Anderson J. N. Fractionation of hen oviduct chromatin into transcriptionally active and inactive regions after selective micrococcal nuclease digestion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T. L., Drahovsky D. Die Beziehung der enzymatischen Methylierung invers repetitiver DNA Sequenzen zur Transkription in Maus P815 Mastocytoma Zellen. Z Naturforsch C. 1980 Jul-Aug;35(7-8):611–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne M. J., Burdon R. H. The sequence specificity of vertebrate DNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Apr;4(4):1025–1037. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.4.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Price P., Pedrinan L., Acs G. Correlation between hypomethylation of DNA and expression of globin genes in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 15;81(1):53–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C. Methylation of milk-borne and genetically transmitted mouse mammary tumor virus proviral DNA. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):653–662. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Ojala D., Posakony J., Nishiguchi J., Attardi G. Nucleotide sequence of a region of human mitochondrial DNA containing the precisely identified origin of replication. Nature. 1979 Jan 18;277(5693):192–198. doi: 10.1038/277192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings D. J., Tait A., Goddard J. M. Methylated bases in DNA from Paramecium aurelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 20;374(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Brown D. D., Reeder R. H. Composition and structure of chromosomal and amplified ribosomal DNA's of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jul 28;51(2):341–360. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90147-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Mulder C., Fleckenstein B. Methylation of Herpesvirus saimiri DNA in lymphoid tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D., McCarthy B. J. Movement of histones in chromatin induced by shearing. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):405–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Ehrlich K., Mayo J. A. Unusual properties of the DNA from Xanthomonas phage XP-12 in which 5-methylcytosine completely replaces cytosine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 16;395(2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Stabel S., Doerfler W. Revertants of adenovirus type 12-transformed hamster cell line T637 as tools in the analysis of integration patterns. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.41-49.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. D., von Hippel P. H. Effects of methylation on the stability of nucleic acid conformations. Studies at the polymer level. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):927–934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geier G. E., Modrich P. Recognition sequence of the dam methylase of Escherichia coli K12 and mode of cleavage of Dpn I endonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1408–1413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri C. P., Gorovsky M. A. DNase I sensitivity of ribosomal genes in isolated nucleosome core particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):197–214. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.197-e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Hattman S., Pleger G. L. ( 6 N)methyl adenine in the nuclear DNA of a eucaryote, Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Cell Biol. 1973 Mar;56(3):697–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A. Macro- and micronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis: a model system for studying the structure and function of eukaryotic nuclei. J Protozool. 1973 Feb;20(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1973.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grantham R. Viral, prokaryote and eukaryote genes contrasted by mRNA sequence indexes. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Brooks J. E., Masurekar M. Sequence specificity of the P1 modification methylase (M.Eco P1) and the DNA methylase (M.Eco dam) controlled by the Escherichia coli dam gene. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S. DNA methylation of T-even bacteriophages and of their nonglucosylated mutants: its role in P1-directed restriction. Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattman S., Kenny C., Berger L., Pratt K. Comparative study of DNA methylation in three unicellular eucaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1156–1157. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1156-1157.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Oudet P., Chambon P. Animal DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Studies on the binding of mammalian RNA polymerases AI and B to Simian virus 40 DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 16;41(2):397–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Hecht N. Methylation of Lilium DNA during the meiotic cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 29;238(1):50–59. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries S. E., Young D., Carroll D. Chromatin structure of the 5S ribonucleic acid genes of Xenopus laevis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 24;18(15):3223–3231. doi: 10.1021/bi00582a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Allfrey V. G., Bradbury E. M., Matthews H. R. Altered nucleosome structure containing DNA sequences complementary to 19S and 26S ribosomal RNA in Physarum polycephalum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1116–1120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalousek F., Morris N. R. The purification and properties of deoxyribonucleic acid methylase from rat spleen. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1157–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W. The 5-methylcytosine content of DNA: tissue specificity. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Aug;78(1):33–36. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040780106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodarev N. N., Votrin I. I., Sokolov N. N., Basnak'ian A. G. Metilirovanie DNK zhromatina i ego rasshcheplenie v izolirovannykh kletochnykh iadrakh pecheni krys. Biokhimiia. 1979 Jun;44(6):1058–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. T., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: correlation with DNase I sensitivity of chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2105–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Complementary specificity of restriction endonucleases of Diplococcus pneumoniae with respect to DNA methylation. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jul;114(1):153–168. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Wilson B., Dixon G. H. Limited action of micrococcal nuclease on trout testis nuclei generates two mononucleosome subsets enriched in transcribed DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1682–1686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: organ specific variations in the methylation pattern within and around ovalbumin and other chicken genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2081–2103. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D., Oudet P., Chambon P. Structure of transcribing chromatin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:1–55. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60670-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Ginder G. D. Specific DNA methylation sites in the vicinity of the chicken beta-globin genes. Nature. 1979 Aug 2;280(5721):419–420. doi: 10.1038/280419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer M., Beck E., Hansen F. G., Bergmans H. E., Messer W., von Meyenburg K., Schaller H. Nucleotide sequence of the origin of replication of the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):580–584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Karpov V. L., Bavykin S. G. The structure of nucleosomes: the arrangement of histones in the DNA grooves and along the DNA chain. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):149–155. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. P., Albright S. C., Garrard W. T. Nucleosome arrangement with regard to DNA base composition. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9194–9199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakhomova M. V., Zaitseva G. N., Belozerskii A. N. Nalichie 5-metiltsitozina i 6-metilaminopurina v sostave DNK nekorotykh vodoroslei. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1968 Sep 21;182(3):712–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Cedar H. Selective degradation of integrated murine leukemia proviral DNA by deoxyribonucleases. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90304-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae P. M., Steele R. E. Modified bases in the DNAs of unicellular eukaryotes: an examination of distributions and possible roles, with emphasis on hydroxymethyluracil in dinoflagellates. Biosystems. 1978 Apr;10(1-2):37–53. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(78)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Cedar H. Distribution of 5-methylcytosine in chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2725–2728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R., Jones A. Genomic transcriptional activity and the structure of chromatin. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):495–500. doi: 10.1038/260495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Nucleosome structure of Xenopus oocyte amplified ribosomal genes. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4908–4916. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. Structure of Xenopus ribosomal gene chromatin during changes in genomic transcription rates. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):709–722. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly J. G., Braun R., Thomas C. A., Jr Methjylation in Physarum DNA. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80638-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell G. J., Walker P. M., Elton R. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Doublet frequency analysis of fractionated vertebrate nuclear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheid B., Srinivasan P. R., Borek E. Deoxyribonucleic acid methylase of mammalian tissues. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):280–285. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal R. P. Ion-exlusion chromatography: analysis and isolation of nucleic acid components, and influence of separation parameters. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Oct;152(2):800–810. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90276-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solage A., Cedar H. Organization of 5-methylcytosine in chromosomal DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 11;17(14):2934–2938. doi: 10.1021/bi00607a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staron K., Jerzmanowski A., Tyniec B., Urbanska A., Toczko K. Nucleoprotein chromatin subunit from Physarum polycephalum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto K., Oka A., Sugisaki H., Takanami M., Nishimura A., Yasuda Y., Hirota Y. Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli K-12 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):575–579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter D., Doerfler W. Methylation of integrated adenovirus type 12 DNA sequences in transformed cells is inversely correlated with viral gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):253–256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szer W., Shugar D. The structure of poly-5-methylcytidylic acid and its twin-stranded complex with poly-inosinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):174–187. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS A. J., SHERRATT H. S. The isolation of nucleic acid fractions from plant leaves and their purine and pyrimidine composition. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):1–4. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VONHIPPEL P. H., FELSENFELD G. MICROCOCCAL NUCLEASE AS A PROBE OF DNA CONFORMATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Jan;3:27–39. doi: 10.1021/bi00889a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanyushin B. F., Mazin A. L., Vasilyev V. K., Belozersky A. N. The content of 5-methylcytosine in animal DNA: the species and tissue specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 28;299(3):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90264-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Neumann R., Kuhlmann I., Sutter D., Doerfler W. DNA methylation and viral gene expression in adenovirus-transformed and -infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 11;8(11):2461–2473. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.11.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT G. R. Recognition and estimation of 5-methylcytosine in nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1951 May;48(5):581–584. doi: 10.1042/bj0480581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT G. R. The purine and pyrimidine composition of deoxypentose nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1951 May;48(5):584–590. doi: 10.1042/bj0480584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldeck W., Föhring B., Chowdhury K., Gruss P., Sauer G. Origin of DNA replication in papovavirus chromatin is recognized by endogenous endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5964–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly of an active chromatin structure during replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):781–792. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


