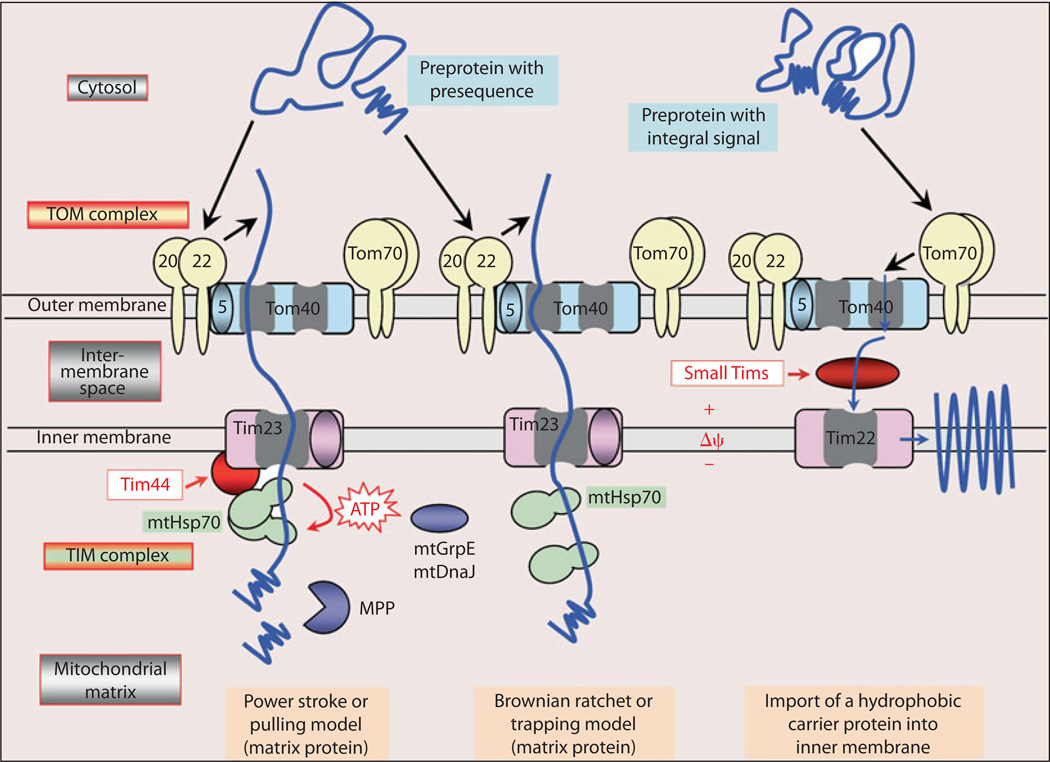
Fig. 3.
Main pathways of protein import into mitochondrial matrix and inner membrane. Mitochondria matrix preproteins with an amino-terminal presequence as well as proteins with integral target sequence translocate through the translocase outer membrane (TOM) complex, made up of 5-, 20-, 22-, 40-and 70-kDa proteins. Preproteins with presequence are translocated across the inner membrane by the Tim23 complex. Two models are proposed: power stroke and Brownian ratchet. The process requires the inner membrane potential (Δψ) and ATP-dependent action of mtHsp70. In the power stroke model, Tim44 seems to function as a membrane anchor of mtHsp70 to the TIM23 complex. The proproteins with integral signals are guided by small Tims proteins across the intermembrane space to the Tim22 complex of the inner membrane and are then inserted into the membrane in a Δψ-dependent step. Tim44 is upregulated in hyperglycemia and its overexpression reduces proteinuria, renal hypertrophy, cell proliferation and apoptosis, and superoxide production in STZ-induced diabetes in CD-1 mice [48–50].