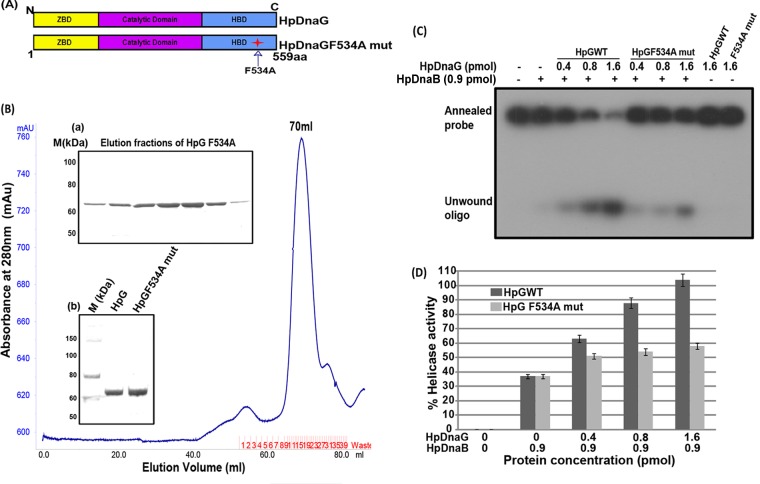
Fig 6.
Purification of HpDnaG F534A mutant and its effect on HpDnaB wild-type helicase activity. (A) Schematic domain organization and site of point mutation in HpDnaG. (B) A gel filtration chromatogram of HpDnaG F534A mutant, as obtained by passing through Hi-Load Superdex-120 ml 16/60 column. Inset panel a shows the elution pattern from the gel filtration of HpDnaG F534A mutant, and inset panel b shows the results for HpDnaGwt (lane 2) and HpDnaG F534A mutant (lane 3) on an SDS-PAGE gel, along with that of the protein marker (lane 1). (C) Modulation of HpDnaB helicase activity in the presence of HpDnaGwt and HpDnaG F534A mutant. Different concentrations of HpDnaGwt and HpDnaG F534A mutant proteins were added in the HpDnaB helicase reaction as shown. The positions of the annealed probe and unwound oligonucleotides are shown in figure. The results indicate that the stimulation of HpDnaB helicase activity is reduced by ∼50% in the presence of the mutant protein compared to the HpDnaGwt protein. (D) The results of a quantitative analysis of the data from the gel in panel C are shown in the graph.