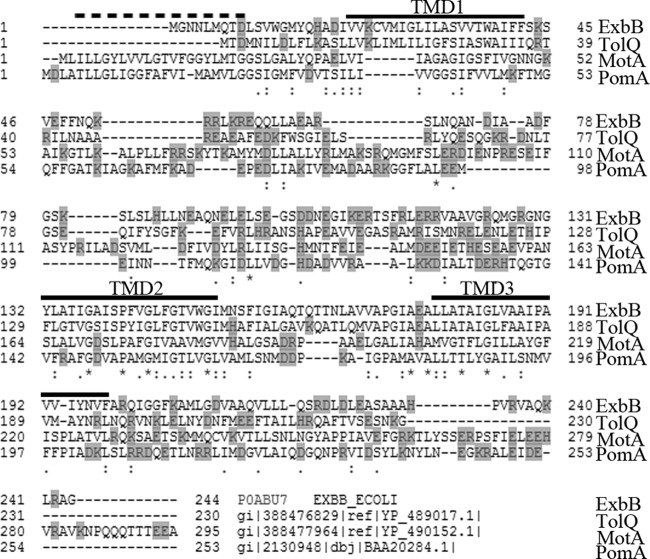
Fig 8.
Sequence alignment of ExbB, TolQ, MotA, and PomA. ExbB, TolQ, MotA, and PomA sequences were aligned using Clustal omega multiple-sequence alignment program (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). Charged residues are shown on a gray background. Predicted ExbB TMDs from Fig. S1 in the supplemental material are indicated by a black bar above the sequence. The dashed bar indicates the predicted location of the MotA/PomA TMD1 (64). ExbB (NCBI accession no. YP_491200.1), TolQ (YP_489017.1), and MotA (YP_490152.1) sequences are from Escherichia coli K-12 strain W3110. The PomA sequence is from Vibrio alginolyticus (GenBank accession no. BAA20284.1).The importance of glycines in alignment of transmembrane domains among these proteins has been recognized previously (59, 92). Gaps introduced to maximize alignment are indicated by dashes in the sequences. Asterisks, colons, and periods indicate identical, conserved, and semiconserved residues, respectively.