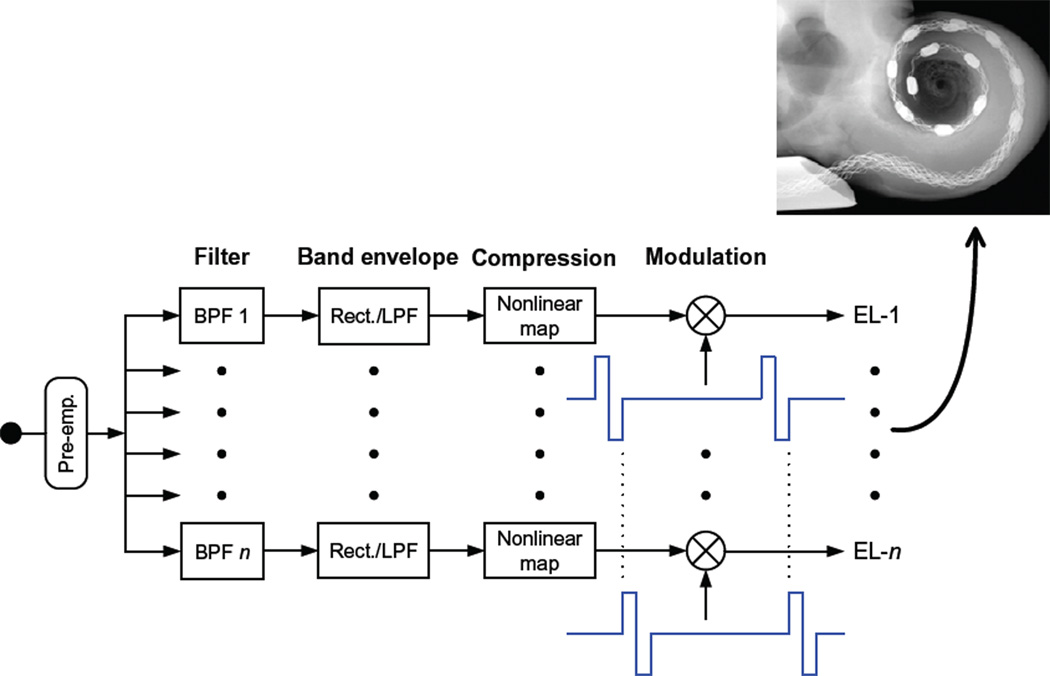
Fig. 1.
Block diagram of the continuous interleaved sampling (CIS) strategy. The input to the strategy is indicated by the filled circle in the left-most part of the diagram. Next, a pre-emphasis filter (Pre-emp.) is used to attenuate strong components in speech below 1.2 kHz. This filter is followed by multiple channels of processing. Each channel includes band-pass filtering (BPF), envelope detection, compression, and modulation. The envelope detectors typically use a rectifier (Rect.) followed by a low-pass filter (LPF). A Hilbert transform or a half-wave rectifier without the LPF also may be used. Carrier waveforms for two of the modulators are shown immediately below the two corresponding multiplier blocks (the circles with an “X” within them). The outputs of the multipliers are directed to intracochlear electrodes (EL-1 to EL-n), as illustrated by the X-ray micrograph in the inset. (Block diagram is adapted from Wilson et al. (1991) with the permission of the Nature Publishing Group. Inset is reproduced from Hüttenbrink et al. (2002) with the permission of Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.)