Fig 2.
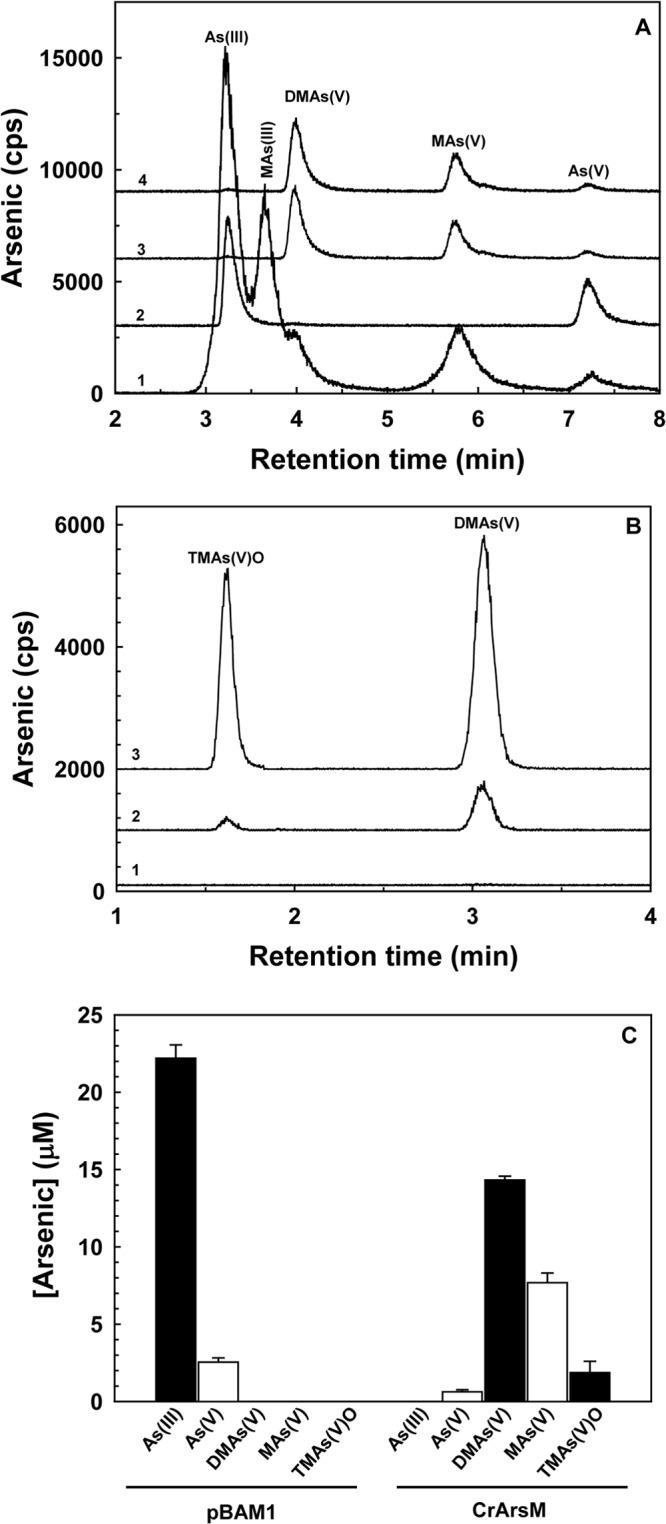
Biotransformation of As(III) in P. putida expressing arsM. (A) Cells of P. putida KT2440 bearing vector plasmid pBAM1 (control) or P. putida KT2440 with arsM stably integrated into the chromosome were grown overnight in Luria-Bertani medium with 25 μM As(III). Arsenical species in solution were separated and identified by anion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS). Curve 1, standards; curve 2, P. putida cells bearing pBAM1 incubated with As(III); curve 3, P. putida with integrated arsM incubated with As(III); curve 4, P. putida with integrated arsM incubated with 25 μM As(V). (B) Volatilization of arsenic by P. putida with integrated arsM for 0 (curve 1), 12 h (curve 2), or 48 h (curve 3) was determined by trapping the gas on H2O2-impregnated filters, elution, and separation of species by HPLC–ICP-MS using an anion-exchange column. (C) After 48 h of growth with 25 μM As(III) in LB medium, arsenic species in solution produced by P. putida bearing pBAM1 (left) or with integrated arsM (right) were quantified by HPLC–ICP-MS. Data are means ± SE (n = 3 experiments).
