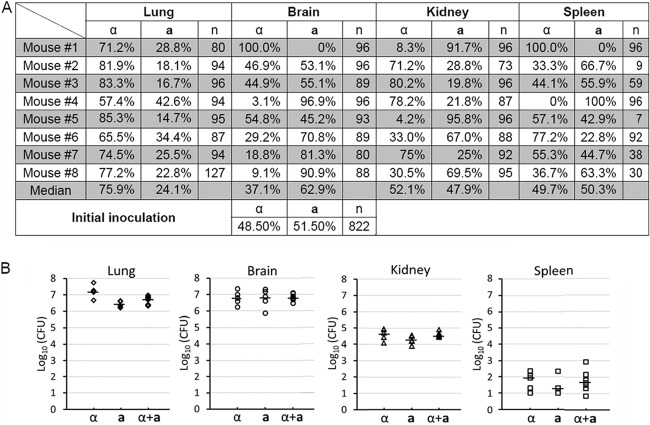
Fig 6.
The mating type distribution during a-α coinfection in the inhalation infection model of cryptococcosis. (A) Animals were challenged with the mixture of a-α fungal cells (1 × 106/animal) by inhalation. At the time of termination, lungs, brains, kidneys, and spleens from eight animals per group were dissected and homogenized. The mating type of randomly picked Cryptococcus cells recovered from each organ was determined. (B) Animals were challenged with 1 × 106 fungal cells (α, a, or the a-α mixture) intranasally. At the time of termination, lungs, brains, kidneys, and spleens from five animals per group were dissected and homogenized. Serial dilutions of the homogenized tissue were plated, and CFU were used to determine the organ fungal burden. The short, bold, horizontal lines indicate the median. The fungal burden of these groups was statistically different in the lungs (P = 0.001). No statistically significant difference was found among the groups in the brain (P = 0.973), the kidney (P = 0.110), or the spleen (P = 0.575).