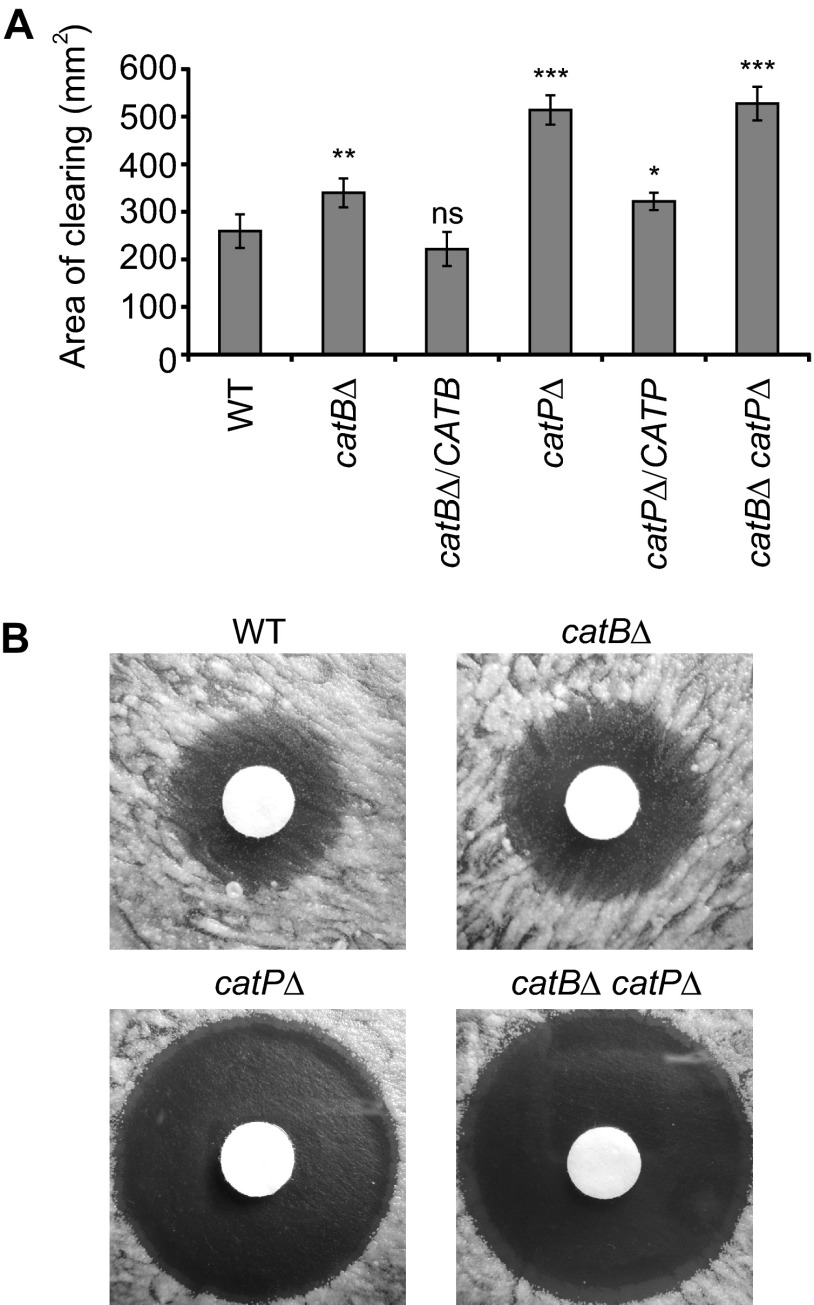
Fig 4.
CatB and CatP provide protection to yeasts from H2O2 in vitro. Resistance of wild-type and catalase-deficient yeasts to killing by H2O2. H2O2 killing of yeast was determined by a filter disk diffusion assay on solid medium using filters with 300 mM H2O2. (A) Quantitation of the sensitivity to H2O2. The zone of clearing around the disks was determined as the total area lacking yeast cell growth. Data presented are the average areas of clearing for three replicate tests, with error bars representing standard deviations. Asterisks represent significant differences from the wild-type strain determined by Student's t test (ns, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (B) Images of Histoplasma yeast growth around H2O2-saturated disks showing the presence of microcolonies of surviving yeasts in zones of clearing for wild type and for CatB-deficient strains but not for strains lacking CatP (catPΔ or catBΔ catPΔ strains). WT, wild type (OSU45); catBΔ, catB mutant (OSU16); catBΔ/CATB, complemented catB mutant (OSU51); catPΔ, catP mutant (OSU157); catPΔ/CATP, complemented catP mutant (OSU158); catBΔ catPΔ, catB catP double mutant (OSU159).