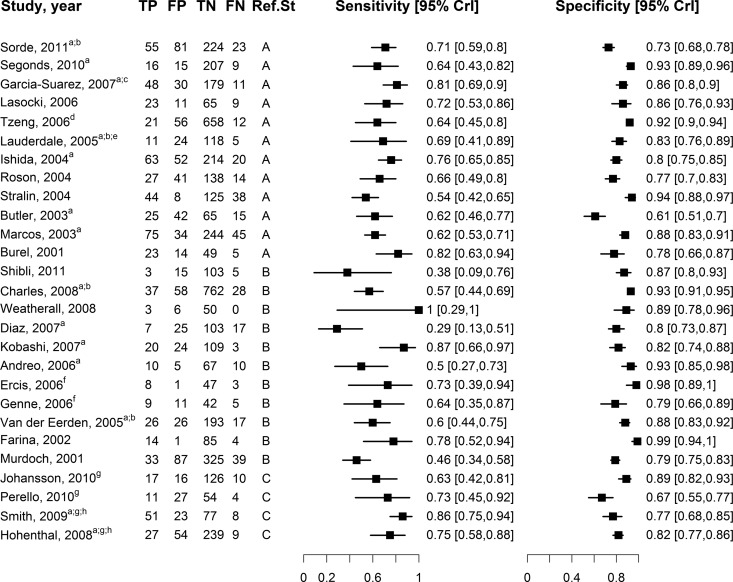
Fig 1.
Forest plot, showing sensitivities and specificites of BinaxNOW-SP with respect to the reference standard in the studies included in our meta-analysis. Studies are ordered by date in descending order and grouped according to reference classes: A (11 studies), B (12 studies), C (4 studies). Footnotes: a, definite and probable S. pneumoniae pneumonia cases were combined into a single category of S. pneumoniae pneumonia; b, authors' definition of S. pneumoniae included a positive BinaxNOW-SP result. and patients diagnosed solely on the basis of a positive BinaxNOW-SP were reclassified as having false-positive results; c, results from the total number of CAP cases derived from the summation of the authors' categories of “pneumococcal infection, pneumonia,” “pneumococcal infection, probable pneumococcal pneumonia,” “nonpneumococcal infections, pneumonia,” and “unknown etiology pneumonia”; d, data included for those patients with lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs); e, analysis restricted to a subset of patients with complete data; f, data used from those patients with CAP, and data from control patients were omitted; g, complete data to construct a two-by-two table provided only for positive blood culture as a reference standard; h, results for the total number of CAP cases were derived from the summation of the authors' categories of “pneumococcal bacteremia, with pneumonia” and “nonbacteremic pneumonia, combined subtotal.”