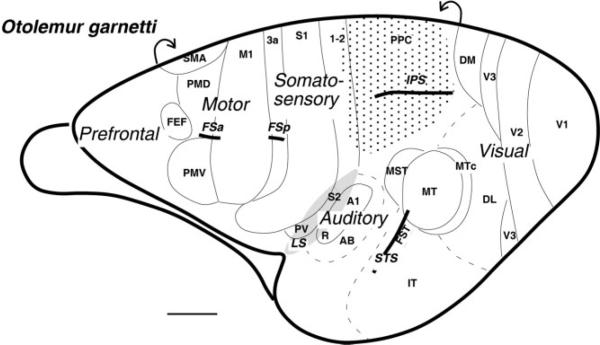
Figure 1.
Subdivisions of the galago cortex shown on the lateral aspect of the left hemisphere. The region of cortex explored in the present study is shaded with dots. Motor areas are based on Wu et al. (2000) and Fang et al. (2005) and include the primary motor cortex (M1), the dorsal and ventral premotor areas (PMD and PMV), supplementary motor area (SMA), and frontal eye field (FEF). Somatosensory areas are from Wu and Kaas (2003) and include primary (S1) and secondary (S2) somatosensory areas, areas 1 and 2, and ventral somatosensory area (PV). Visual areas are from Lyon and Kaas (2002) and include primary visual area (V1), second (V2) and third (V3) visual areas, dorsolateral (DL) and dorsomedial (DM) visual areas, middle temporal (MT) and middle temporal crescent (MTc) areas, middle superior temporal area (MST), fundal superior temporal area (FST), and inferotemporal area (IT). Auditory areas are from Kaas and Hackett (2000) and include primary auditory cortex (A1), rostral primary auditory area (R), and auditory belt (AB). Part of auditory belt is hidden in the lateral sulcus. The partially opened lateral sulcus (LS) is shaded. The intraparietal sulcus (IPS), the superior temporal sulcus (STS), the frontal anterior (FSa), and the posterior (FSp) sulci are indicated. Scale bar = 5 mm.