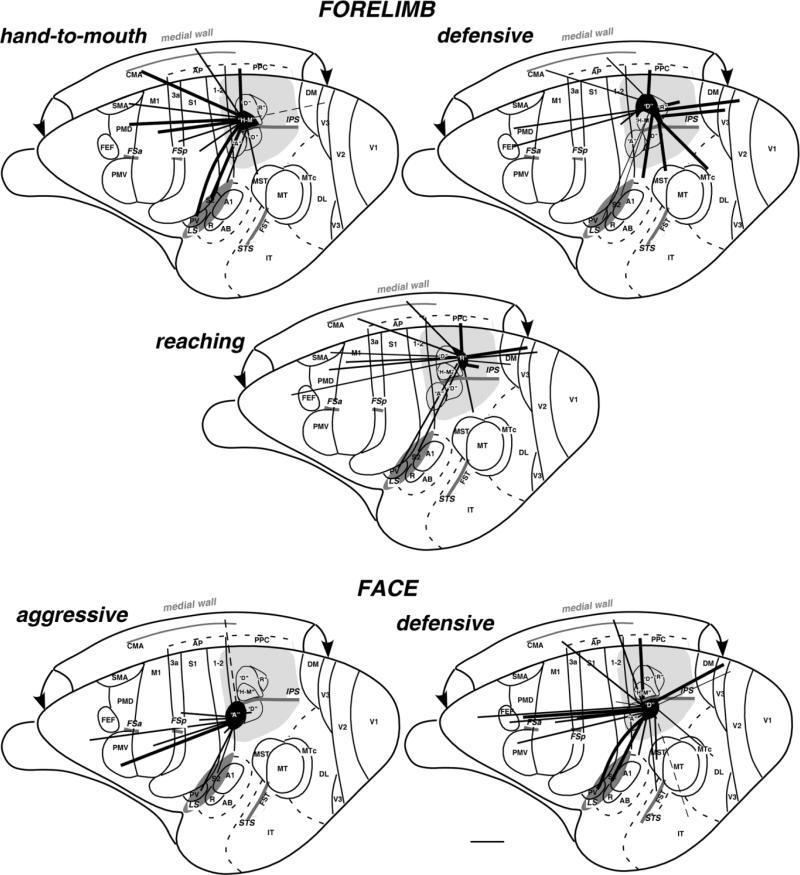
Figure 13.
Summary of corticocortical connections of the specific complex movement zones of PPC in galago brain. Functionally distinct movement zones (filled with black) and their connections (indicated by black lines) are marked on the exposed left cerebral hemisphere. Thick lines represent strong connections, and thin lines represent weak connections. Note that the hand-to-mouth zone has major connections with somatosensory and motor fields, while being isolated from direct auditory and visual inputs, whereas reaching and especially defensive forelimb zones get fewer somatosensory or motor inputs but more information from nonprimary visual areas. Face defensive and aggressive zones below the IPS receive major inputs from motor, premotor, and somatosensory areas (3a, 3b, 1-2, S2, PV). The defensive face zone receives additional input from nonprimary visual areas (e.g., V3). Sulci are marked with dark gray, and the entire region explored by ICMS is marked with light gray. A, aggressive; D, defensive forelimb or face; H-M, hand-to-mouth; R, reach. Scale bar = 5 mm.