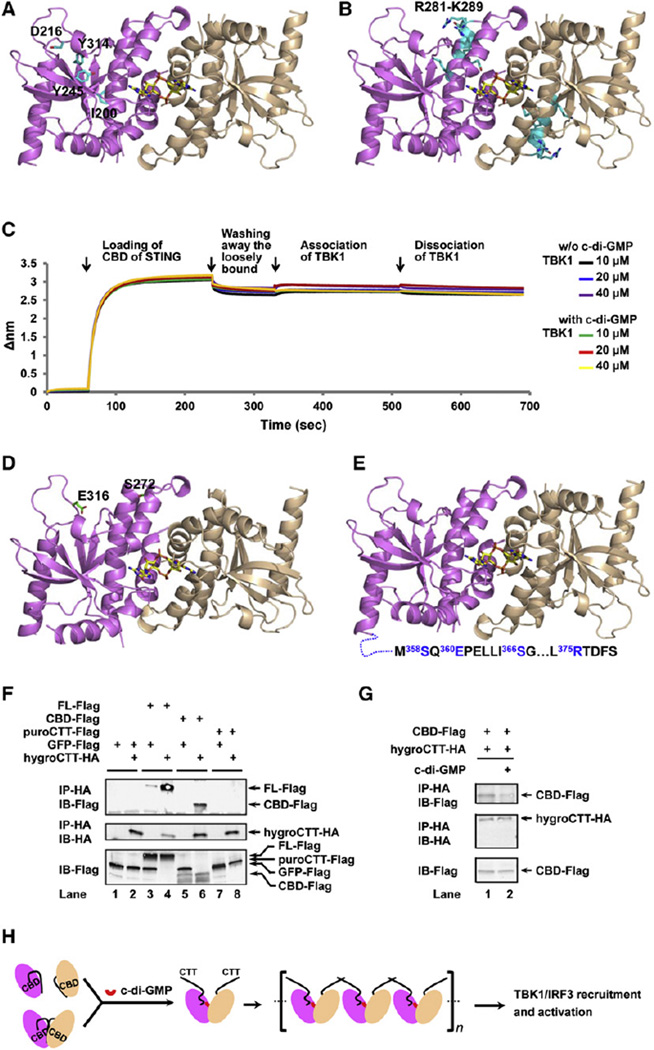
Figure 5. Proposed Mechanism of STING Activation.
(A) Mutants that contain buried residues and fail to interact with c-di-GMP. These buried residues, I200, D216, Y245, and Y314, are shown as sticks on a cartoon representation of the STING/c-di-GMP structure.
(B) A multiply substituted mutant that contains exposed residues and fails to interact with c-di-GMP. These residues,R281–K289,are coloredincyanand shownassticks.
(C) Real time biolayer interferometry measurement of 10, 20, and 40 µM TBK1 to immobilized STING CBD in the absence (black, blue, and purple lines) or presence (green, red, and yellow lines) of c-di-GMP. Biotinylated STING CBD loading and washing as well as TBK1 association and dissociation curves are labeled.
(D) Mutants that bind c-di-GMP, hyperinduce IFN but do not respond to c-di-GMP for further enhancement of IFN production. These residues, E316 and S272, are shown as sticks on the STING/c-di-GMP cartoon representation.
(E) Mutants in the CTT that bind c-di-GMP, induce IFN but do not respond to c-di-GMP for further enhancement of IFN production. These residues, S358/E360/S366 and R375 are highlighted in blue in the appended CTT.
(F) Interaction of CTT with full-length (FL) cytosolic domain of STING and CBD were detected by immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by immunoblotting (IB) in 293 cells transfected with indicated expression constructs.
(G) The interaction between CTT and CBD as detected by coimmunoprecipitation is weakened when cells are stimulated with c-di-GMP.
(H) “Release of autoinhibition” model. In unstimulated cells, STING exists in an autoinhibited status with an intramolecular CBD (violet or wheat ovals)/CTT (black curvy lines) interaction, either as a monomer or dimer. Binding of c-di-GMP at the dimer interface displaces CTT, induces and stabilizes STING dimer, and releases STING from autoinhibition. STING dimers with freed CTT may further oligomerize through CTT. Activated STING then recruits and activates TBK1 and IRF3.