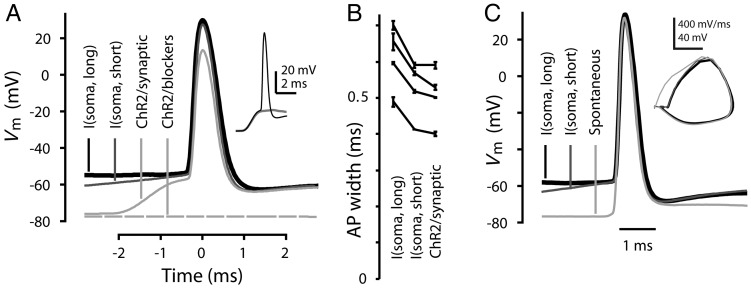
Figure 4.
Width of APs evoked by current steps in corticospinal neurons compared with synaptically evoked and spontaneous APs. (A) Peak-aligned waveforms of APs evoked in a corticospinal neuron either by current steps injected via the somatic patch electrode (I(soma, short) and I(soma, long): 800 pA, 10 ms or 500 pA, 1 s current steps, respectively), or by photoexcitation of ChR2 expressing layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons (ChR2/synaptic). The lowermost trace shows the absence of photo-evoked response after application of 10 μM NBQX, 5 μM CPP, and 10 μM gabazine to block synaptic transmission. Inset: As shown by these subthreshold (gray) and suprathreshold (black) traces, stimulation intensity was near AP threshold (scale: 20 mV, 2 ms). (B) Widths of APs induced by long or short somatic current steps or by synaptic excitation (n = 4 neurons), plotted as mean ± SD, averaged over multiple stimulations (range: 2–7) per neuron. (C) Spontaneously occurring AP waveform compared with APs evoked by brief or prolonged somatic current injection in a corticospinal neuron (animal age P49). Inset: Phase-space representation of the APs.