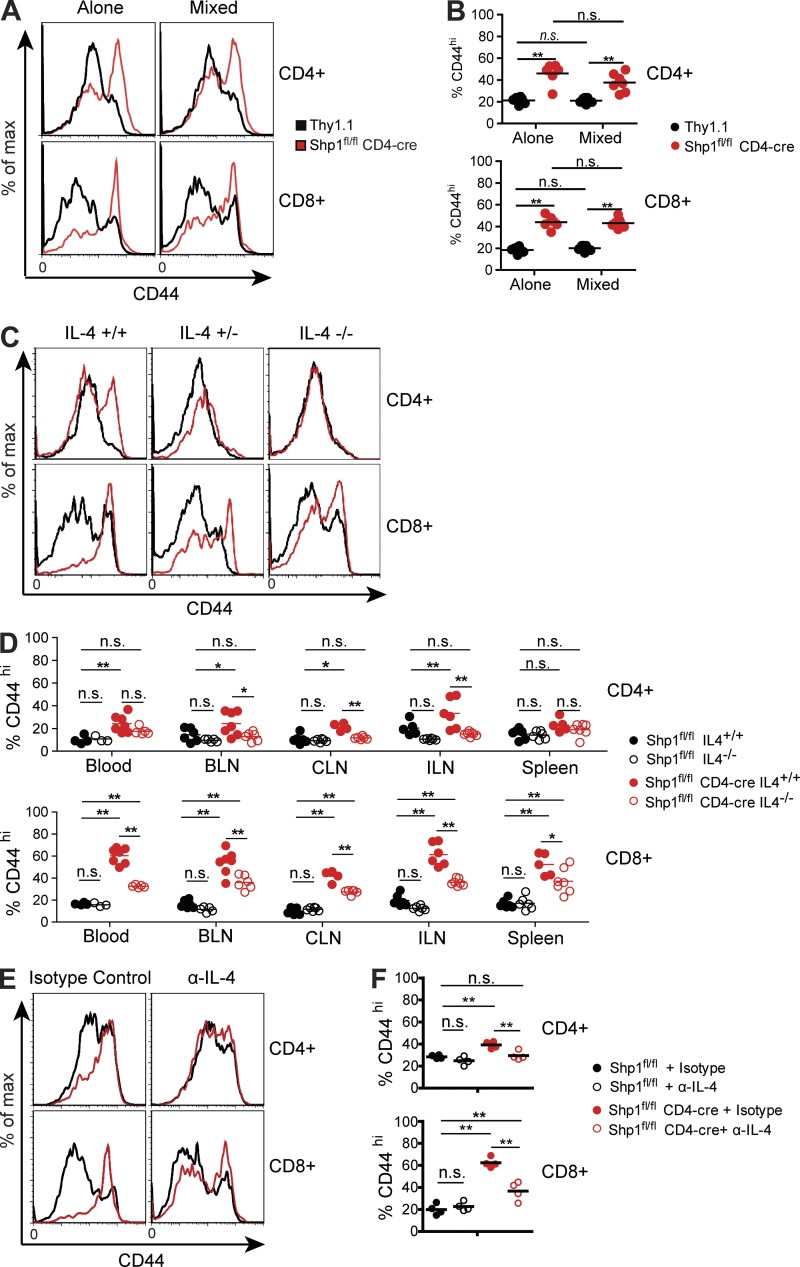
Figure 6.
IL-4 is required for the accumulation of CD44hi T cells in Shp1 conditional knockout mice. (A) Bone marrow from Thy1.1 and/or Shp1fl/fl CD4-cre mice was transferred into irradiated CD45.1 host animals to generate mixed bone marrow chimeras. CD44 expression on splenic T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Flow plots are gated on CD45.2+Thy1.1+Thy1.2− (Thy1.1) or CD45.2+Thy1.1−Thy1.2+ (Shp1 fl/fl CD4-cre) populations, as well as CD4+ or CD8+. (B) Percentage of splenic T cells with a CD44hi phenotype in bone marrow chimeras from A.; n = 6–7. (C) CD44 expression on T cells in the blood of mice of the indicated genotypes. (D) Percentage of T cells with a CD44hi phenotype in the indicated tissues of IL-4 and Shp1-deficient mice; n = 6–7. BLN, brachial LN; CLN, cervical LN; ILN, inguinal LN. (E) CD44 expression of T cells in blood of mice given 200 µg α-IL-4 or an isotype control 5 d before sacrifice. (F) Percentage of T cells with a CD44hi phenotype in the blood of mice treated as in E. Data are representative of two independent experiments; n = 4. Statistical analyses of data in B, D, and F were performed by two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s post-test analysis; ns, P ≥ 0.05; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Horizontal bars for B, D, and F represent sample means.