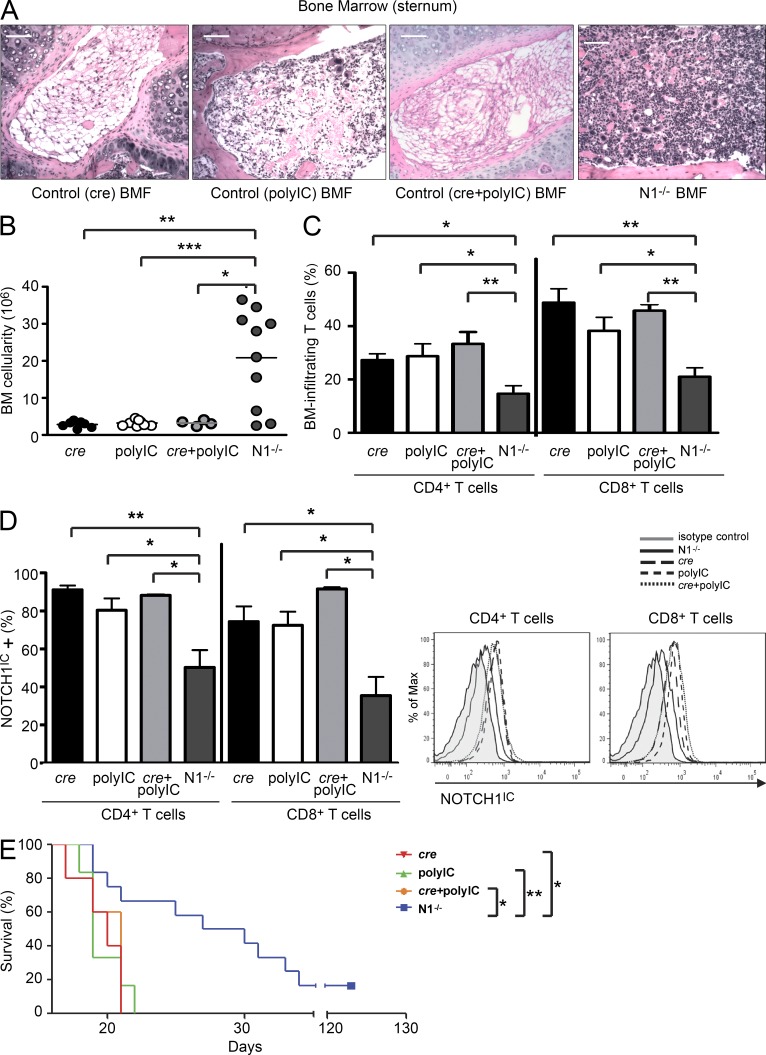
Figure 4.
Conditionally deleting Notch1 ameliorates disease in AA mice. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining of BM from one AA mouse each whose BMF was induced with cre control, polyIC control, cre + polyIC control, or Notch1 conditional KO (N1−/−) splenocytes. Bars, 200 µm. (B and C) BM cellularity (B) and percentages of BM-infiltrating T cells (C) were determined in AA mice induced with N1−/− splenocytes (n = 10) and compared with AA mice induced with cre control (n = 4), polyIC control (n = 6), or cre + polyIC control (n = 4) splenocytes. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of NOTCH1IC in T cells isolated from the BM of cre control (n = 4), polyIC control (n = 6), cre + polyIC control (n = 4), or N1−/− mice after treatment with polyIC. (E) Kaplan–Meier survival estimates of AA mice induced with N1−/− splenocytes (n = 12) compared with animals induced with cre control (n = 6), polyIC control (n = 6), or cre + polyIC control (n = 7) splenocytes. Data represent the mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; unpaired Student’s t test; log-rank test for survival estimates.