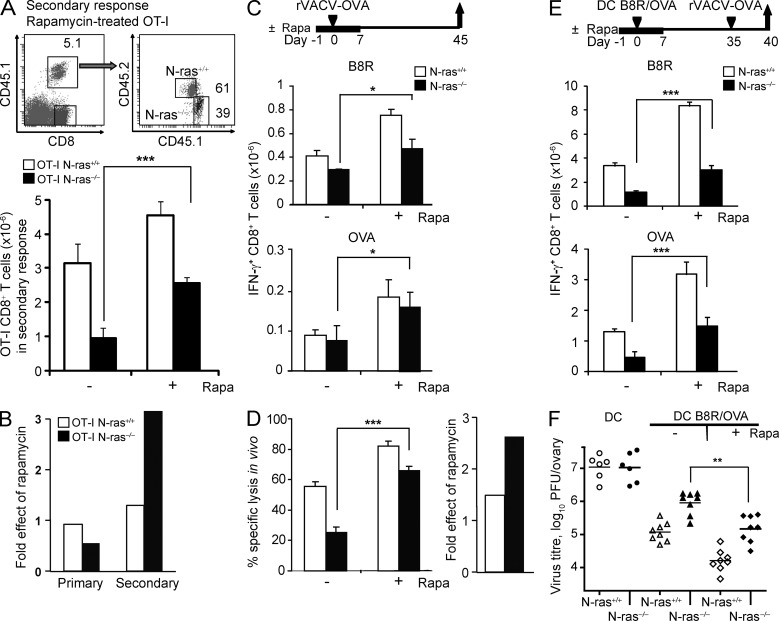
Figure 6.
Inhibition of mTOR in vivo with rapamycin partially rescues the N-ras–deficient CD8+ T cell–intrinsic defects in secondary responses, functional memory, and antiviral protective immunity. (A and B) Following a similar protocol to that depicted in Fig. 5 A for the study of the primary response, N-ras+/+ or N-ras−/− OT-I cells were treated or not with rapamycin and transferred into recipient mice. 1 d before rVACV-OVA infection, daily treatment or no treatment of recipient mice with rapamycin was started and maintained for 6 d. For the study of the secondary response after infection, a protocol similar to that depicted in Fig. 5 B was used, but cells were treated or not with rapamycin. 1 d before DC immunization, daily treatment or no treatment of recipient mice with rapamycin was started and maintained for 8 d. The frequency and numbers of splenic N-ras+/+ and N-ras−/− transgenic OT-I cells were determined 8 d after primary antigen exposure (not depicted) and 5 d after challenge, for which representative dot plots and the mean ± SEM data are shown (A). Fold effect of rapamycin treatment during the primary and secondary responses was calculated as the ratio of mean OT-I cell numbers in treated versus untreated animals (n = 3, two experiments; B). (C and D) WT and N-ras−/− mice were infected as in Fig. 3 A and treated or not with rapamycin as above. On day 45 p.i., IFN-γ production by B8R- and OVA-specific splenic CD8+ T lymphocytes (n = 3, two experiments, results are expressed as mean ± SEM) was determined ex vivo (C), and the cytotoxic activity specific for B8R peptide was assessed in vivo. Fold effect of rapamycin was calculated as in B (n = 3, two experiments, results are expressed as mean ± SEM; D). (E and F) WT and N-ras−/− mice were vaccinated with peptide-loaded mDC as in Fig. 4 A and treated or not with rapamycin as above. On day 35, mice were infected with rVACV-OVA, and 5 d later ex vivo IFN-γ production by B8R- and OVA-specific splenic CD8+ T lymphocytes was analyzed as a measure of functional secondary responses (n = 4, two experiments; E), whereas determination of infectious virus titers in the ovaries detected protective immunity (F). Horizontal bars show the mean values. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.005; ***, P < 0.0005.